Tworzenie oprogramowania z wykorzystaniem metodyk Agile dla programistów
Jak programiści na całym świecie mogą stosować metodyki Agile w codziennej pracy
Zacznij korzystać z bezpłatnego szablonu Jira Scrum
Usprawnij swój projekt i z łatwością planuj i śledź pracę oraz zarządzaj nią w sprintach. Szablon obejmuje tablice, backlogi, harmonogramy, raporty i nie tylko!
Agile dla zespołów programistycznych
Podejście Agile zmieniło sposób projektowania, tworzenia i wysyłania oprogramowania. Dla programistów to coś więcej niż ceremonie i narzędzia — to sposób myślenia, który optymalizuje naukę, jakość i przepływ.
Zespoły Agile pracują w małych, zweryfikowanych krokach, ciągle się integrują i akceptują zmiany, nie destabilizując procesu dostarczania oprogramowania. W tym omówieniu wyjaśniono, dlaczego podejście Agile jest istotne dla programistów i jak przejawia się w codziennej pracy oraz przedstawiono pięć praktyk ukierunkowanych na programistów, które pomagają zespołom osiągać sukces.
Dlaczego metodyka Agile jest ważna dla programistów
Metodologia Agile jest ważna dla programistów, ponieważ umożliwia szybkie dostosowywanie się do zmieniających się wymagań przez iteracyjne tworzenie oprogramowania. Kładąc nacisk na współpracę i elastyczność, Agile pomaga zespołom wydajniej dostarczać oprogramowanie o wyższej jakości. Oto kilka innych zalet Agile dla zespołów programistycznych:
Chroni jakość bez kompromisów między sukcesem projektu a pracą zespołu ponad siły: Agile dostosowuje zakres pod kątem jakości. Dostarczając oprogramowanie etapami i koncentrując się na jasnym określeniu tego, co jest gotowe, programiści unikają kryzysu przepracowania przed końcem projektu i ograniczają regresje.
Umożliwia utrzymanie zrównoważonego tempa: iteracje ograniczają ryzyko integracji typu big bang i pozwalają zespołom zachować niezłą przepustowość i morale.
Poprawia zgodność i przejrzystość: częsta współpraca z zespołami produktowymi, projektowymi, QA i operacyjnymi ogranicza tworzenie nowych wersji, objaśnia kryteria akceptacji i pomaga zespołom wysyłać to, czego użytkownicy faktycznie potrzebują.
Bezpiecznie wprowadza zmiany: iteracyjne odkrywanie, szybka informacja zwrotna i częste wydania umożliwiają bezpieczne dostosowywanie priorytetów w miarę pojawiania się analiz dotyczących klientów.
Kontroluje dług techniczny: praktyki takie jak przegląd kodu, ciągła integracja, automatyczne testowanie i małe rozmiary partii zapewniają dobrą kondycję bazy kodu i możliwość jej utrzymania.
Jak programiści stosują metodologię Agile
1. Iteracyjny rozwój dzięki historyjkom użytkowników i sprintom
Metodologia Agile zmieniła sposób, w jaki programiści tworzą i dostarczają produkty. Wiemy, że pomaga ona położyć nacisk na współpracę, elastyczność, ciągłe doskonalenie i krótszy czas reakcji. Oto kilka dodatkowych sposobów stosowania przez programistów zasad Agile w codziennej pracy:
1. Iteracyjny rozwój dzięki historyjkom użytkowników i sprintom
Programiści dzielą pracę na historyjki użytkowników z jasnymi kryteriami akceptacji i wdrażają je w krótkich iteracjach. Każdy sprint ma na celu wygenerowanie potencjalnie nadającego się do wysyłki przyrostu, uwidaczniając postępy i umożliwiając terminową informację zwrotną.
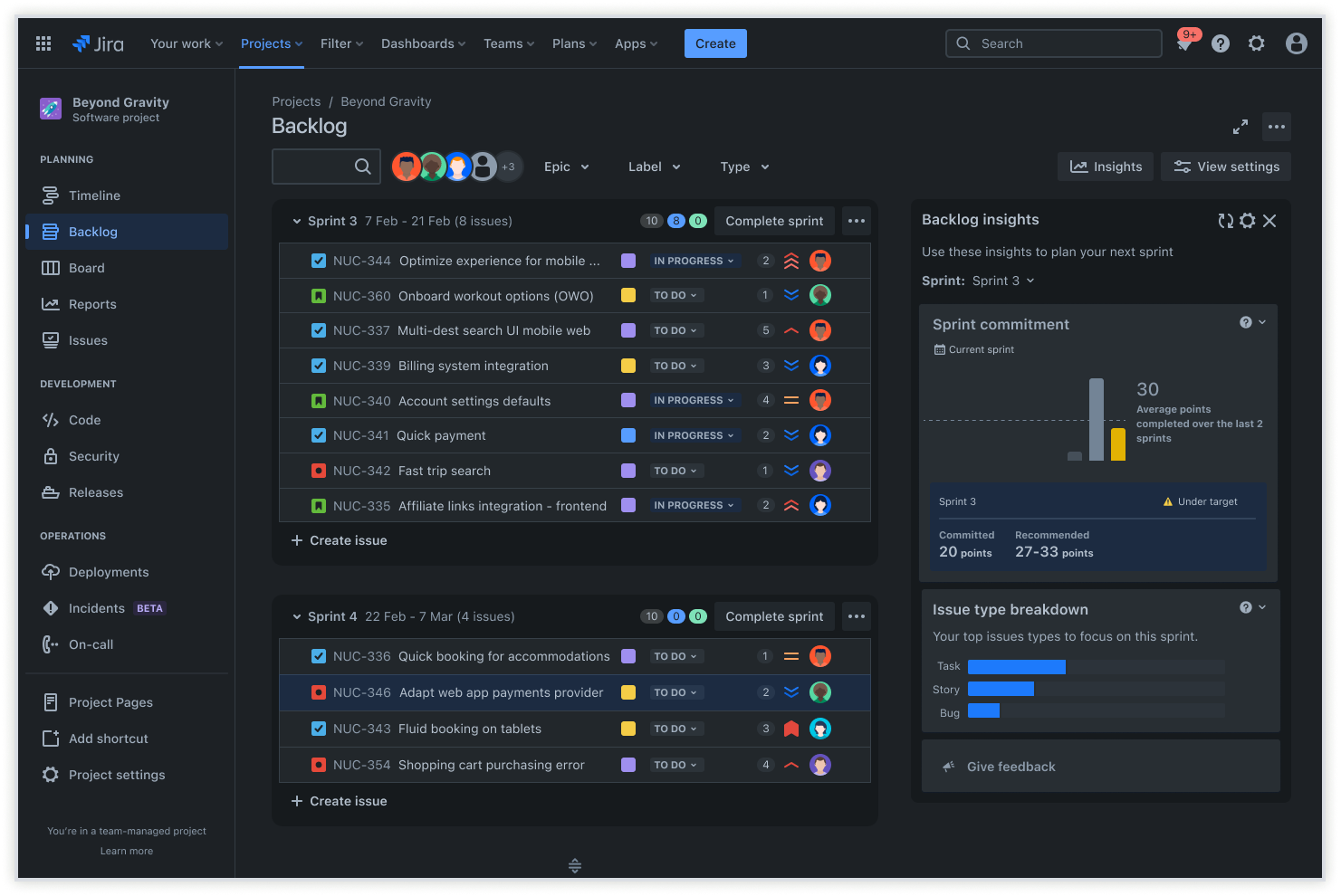
This is where a seamless and visible sprint backlog is crucial for software developers. This view keeps everyone aligned on priorities and progress—especially with clear user stories.
When the backlog is easy to access and up to date, team members can quickly see what needs to be done, who’s working on what, and how work is moving forward. This transparency helps prevent misunderstandings, reduces bottlenecks, and makes it easier to adapt to changes.
2. Współpraca i samoorganizacja
Zespoły Agile samodzielnie organizują się, aby osiągnąć cele sprintu. Programiści aktywnie uczestniczą w porządkowaniu rejestru zadań oraz szacowaniu i ustalaniu priorytetów, a także współpracują podczas codziennych spotkań stand-up, przeglądów sprintów i retrospektyw, aby ciągle poprawiać przepływ pracy i jakość.
Znaczenie jasnego określenia ról
3. Strategie tworzenia gałęzi i kontrola wersji
Zespoły korzystają z przepływów pracy Git, które obejmują gałęzie funkcjonalne, gałęzie krótkotrwałe oraz chronione gałęzie główne, aby izolować zmiany, umożliwiać pracę równoległą i zmniejszyć ryzyko konfliktów podczas scalania. Pull requesty zapewniają ustrukturyzowaną weryfikację oraz możliwość śledzenia zmian od pomysłu aż do scalenia.
Szukasz więcej informacji? Dowiedz się, jak Git wpisuje się w przepływy pracy Agile dla programistów w tym przydatnym artykule.
4. Ciągła integracja, testowanie i gotowość do wydania
Programiści przeprowadzają częste integracje. Każdy commit uruchamia zautomatyzowane kompilacje i testy. Pozwala to wcześnie wykrywać defekty, utrzymuje gotowość głównej gałęzi do wdrożenia i skraca pętle informacji zwrotnej.
Pipeline'y wydań automatyzują pakiety, promocję środowiska i weryfikację. Ale nic z tego nie jest możliwe bez wdrożenia najlepszych praktyk ciągłej integracji.
5. Dług techniczny i reakcja na incydenty jako najważniejsza praca
Zespoły Agile traktują odporność i łatwość konserwacji jako cechy produktu. Programiści planują refaktory, spłacają dług techniczny i stosują nienaganną reakcję na incydenty. Skraca to przyszły czas cyklu i zwiększa przekonanie do zmian.
5 najlepszych praktyk dla twórców oprogramowania w zakresie stosowania metodyki Agile
Każdy zespół ma własne unikalne podejście do Agile, ale istnieje kilka wskazówek, których warto przestrzegać, aby stosować tę metodologię płynniej i szybciej.
1. Zastosowanie przepływu pracy, w którym gałąź jest tworzona dla każdego zadania za pomocą metodycznych pull requestów
Dzięki solidnej strategii tworzenia gałęzi baza kodów pozostaje w dobrej kondycji, a zespół jest produktywny. Stwórz osobną gałąź dla każdej historyjki, każdego błędu lub krótkiego impulsu i utrzymuj krótkotrwałość gałęzi, aby uniknąć dryfowania kodu.
Użyj szablonów pull requestów, aby zapewnić kontekst, w tym zakres, zrzuty ekranu, testy i plany wdrażania. Zawsze wymagaj co najmniej jednej oceny przez współpracownika i upewnij się, że wszystkie kontrole CI zakończą się przed scaleniem.
Porada eksperta
2. Stworzenie solidnego zabezpieczenia dzięki zautomatyzowanym testom i ciągłej integracji
Solidne zabezpieczenie zaczyna się od zautomatyzowanych testów i ciągłej integracji. Dąż do zrównoważonej piramidy testowej: postaw na szybkie testy jednostkowe, dodaj ukierunkowane testy komponentów lub testy kontraktowe i zachowaj zgodne z zasadami lean i krótkie testy kompleksowe.
Przeprowadzaj wszystkie testy każdego commitu za pomocą ciągłej integracji, aby wcześnie wykrywać problemy, oraz skróć czas kompilacji, aby programiści pozostali produktywni. Zautomatyzuj analizę statyczną, skanowanie zabezpieczeń i linting, aby wykryć wady przed przeglądem kodu, dzięki czemu baza kodu jest bezpieczniejsza i bardziej niezawodna.
3. Określenie i uszanowanie „ukończenia”
Staranne zdefiniowanie ukończenia (DoD) powinno obejmować: wdrożony kod, dodane i zakończone powodzeniem testy, sprawdzony kod, kontrole bezpieczeństwa i jakości oznaczone na zielono, zaktualizowaną dokumentację oraz zdefiniowane przełączniki funkcji lub plan wdrożenia.
Zapewnij widoczność definicji ukończenia (DoD) w repozytorium lub projekcie i wykorzystaj automatyzację (obowiązkowe kontrole, zabezpieczenia gałęzi), aby egzekwować jej przestrzeganie w sposób spójny i konsekwentny.

4. Traktowanie długu technicznego jako elementu backlogu
Traktuj refaktory i dług techniczny jako najważniejsze elementy backlogu. To zapewni im jasne kryteria akceptacji i mierzalne wyniki, takie jak krótszy czas kompilacji lub mniej niespójnych testów.
W każdym sprincie przeznacz czas na konserwację, niezawodność i pracę nad wydajnością, używając budżetów błędów lub wskaźników operacyjnych do pomocy w nadaniu priorytetu temu, co najważniejsze.
5. Zamknięcie pętli dzięki danym — planowanie, mierzenie i uczenie się
Używaj umów zespołowych oraz celów sprintu, aby utrzymać zespół skoncentrowany na wynikach, które przynoszą realną wartość dla użytkowników i wywołują zauważalne zmiany w zachowaniu, a nie tylko na realizacji zadań. Śledź wskaźniki takie jak czas cyklu, prace w toku, wskaźnik niezauważonych wad, wskaźnik błędnych zmian oraz średni czas przywracania sprawności.
Pomoże to w prowadzeniu ciągłego doskonalenia oraz znaczących eksperymentów podczas retrospektyw w zespole programistycznym.
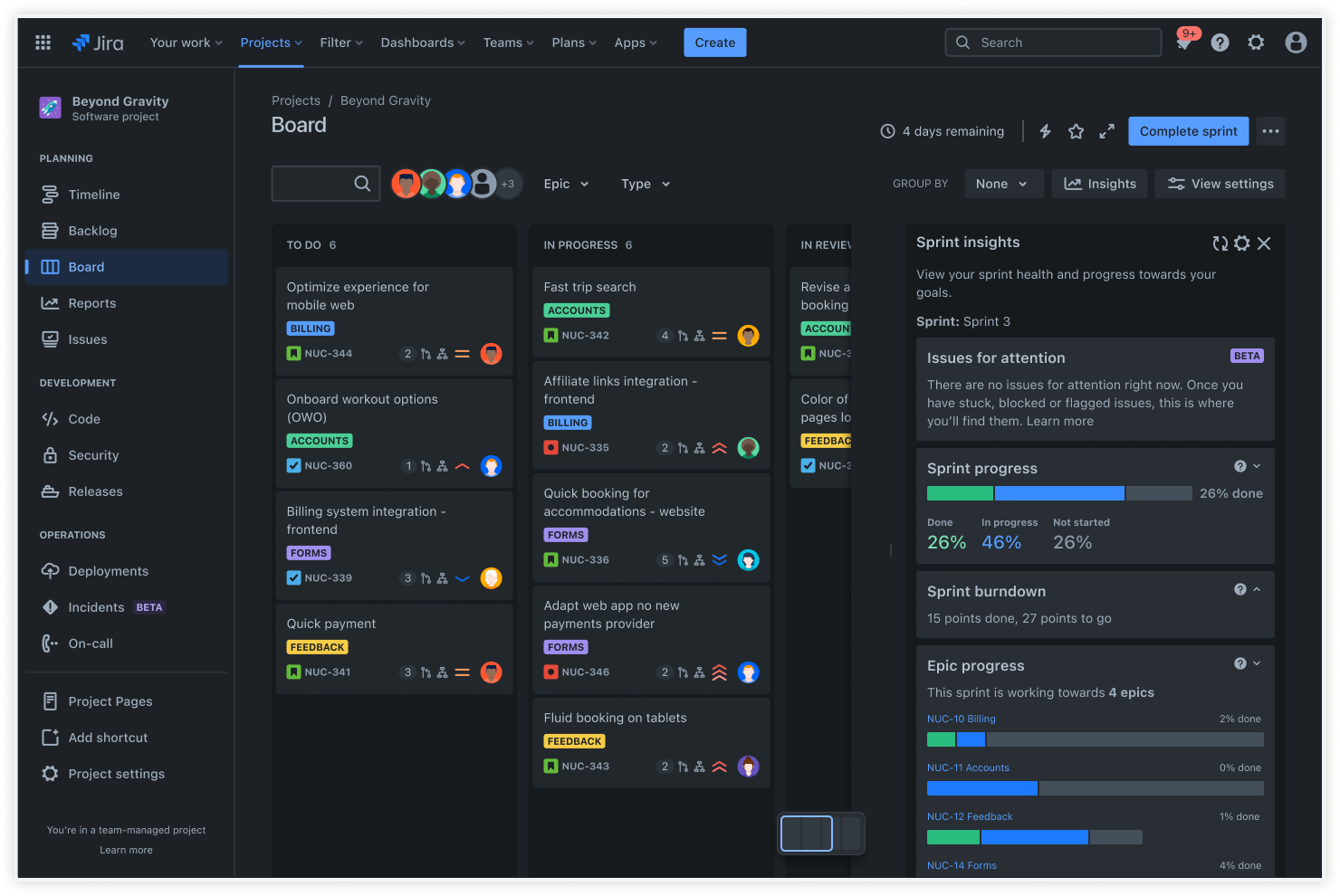
Integracja informacji dla zespołów programistycznych
Agile pomaga programistom dostarczać wartość na każdym etapie, jednocześnie zapewniając płynne działanie systemów. Operując na małych, przystępnych elementach oraz wcześnie testując i integrując, zespoły mogą przyspieszyć pracę.
Wspólne przeglądanie kodu i kontrolowanie na bieżąco długu technicznego pomaga wszystkim nabrać przekonania do każdej zmiany. Natomiast Jira pozwala jeszcze łatwiej śledzić postępy, szybko uzyskiwać informację zwrotną i sprawić, że wszyscy są na bieżąco.
Jaki jest tego efekt?
Lepsze oprogramowanie, bardziej zadowolone zespoły i swoboda wysyłania mniejszych partii, szybszego uczenia się i rozwiązywania problemów — to przewaga Agile dzięki Jirze.
Tworzenie oprogramowania z wykorzystaniem metodyk Agile dla programistów
Jak programiści na całym świecie mogą stosować metodyki Agile w codziennej pracy
Zacznij korzystać z bezpłatnego szablonu Jira Scrum
Usprawnij swój projekt i z łatwością planuj i śledź pracę oraz zarządzaj nią w sprintach. Szablon obejmuje tablice, backlogi, harmonogramy, raporty i nie tylko!
Agile dla zespołów programistycznych
Podejście Agile zmieniło sposób projektowania, tworzenia i wysyłania oprogramowania. Dla programistów to coś więcej niż ceremonie i narzędzia — to sposób myślenia, który optymalizuje naukę, jakość i przepływ.
Zespoły Agile pracują w małych, zweryfikowanych krokach, ciągle się integrują i akceptują zmiany, nie destabilizując procesu dostarczania oprogramowania. W tym omówieniu wyjaśniono, dlaczego podejście Agile jest istotne dla programistów i jak przejawia się w codziennej pracy oraz przedstawiono pięć praktyk ukierunkowanych na programistów, które pomagają zespołom osiągać sukces.
Dlaczego metodyka Agile jest ważna dla programistów
Metodologia Agile jest ważna dla programistów, ponieważ umożliwia szybkie dostosowywanie się do zmieniających się wymagań przez iteracyjne tworzenie oprogramowania. Kładąc nacisk na współpracę i elastyczność, Agile pomaga zespołom wydajniej dostarczać oprogramowanie o wyższej jakości. Oto kilka innych zalet Agile dla zespołów programistycznych:
Chroni jakość bez kompromisów między sukcesem projektu a pracą zespołu ponad siły: Agile dostosowuje zakres pod kątem jakości. Dostarczając oprogramowanie etapami i koncentrując się na jasnym określeniu tego, co jest gotowe, programiści unikają kryzysu przepracowania przed końcem projektu i ograniczają regresje.
Umożliwia utrzymanie zrównoważonego tempa: iteracje ograniczają ryzyko integracji typu big bang i pozwalają zespołom zachować niezłą przepustowość i morale.
Poprawia zgodność i przejrzystość: częsta współpraca z zespołami produktowymi, projektowymi, QA i operacyjnymi ogranicza tworzenie nowych wersji, objaśnia kryteria akceptacji i pomaga zespołom wysyłać to, czego użytkownicy faktycznie potrzebują.
Bezpiecznie wprowadza zmiany: iteracyjne odkrywanie, szybka informacja zwrotna i częste wydania umożliwiają bezpieczne dostosowywanie priorytetów w miarę pojawiania się analiz dotyczących klientów.
Kontroluje dług techniczny: praktyki takie jak przegląd kodu, ciągła integracja, automatyczne testowanie i małe rozmiary partii zapewniają dobrą kondycję bazy kodu i możliwość jej utrzymania.
Jak programiści stosują metodologię Agile
1. Iteracyjny rozwój dzięki historyjkom użytkowników i sprintom
Metodologia Agile zmieniła sposób, w jaki programiści tworzą i dostarczają produkty. Wiemy, że pomaga ona położyć nacisk na współpracę, elastyczność, ciągłe doskonalenie i krótszy czas reakcji. Oto kilka dodatkowych sposobów stosowania przez programistów zasad Agile w codziennej pracy:
1. Iteracyjny rozwój dzięki historyjkom użytkowników i sprintom
Programiści dzielą pracę na historyjki użytkowników z jasnymi kryteriami akceptacji i wdrażają je w krótkich iteracjach. Każdy sprint ma na celu wygenerowanie potencjalnie nadającego się do wysyłki przyrostu, uwidaczniając postępy i umożliwiając terminową informację zwrotną.

This is where a seamless and visible sprint backlog is crucial for software developers. This view keeps everyone aligned on priorities and progress—especially with clear user stories.
When the backlog is easy to access and up to date, team members can quickly see what needs to be done, who’s working on what, and how work is moving forward. This transparency helps prevent misunderstandings, reduces bottlenecks, and makes it easier to adapt to changes.
2. Współpraca i samoorganizacja
Zespoły Agile samodzielnie organizują się, aby osiągnąć cele sprintu. Programiści aktywnie uczestniczą w porządkowaniu rejestru zadań oraz szacowaniu i ustalaniu priorytetów, a także współpracują podczas codziennych spotkań stand-up, przeglądów sprintów i retrospektyw, aby ciągle poprawiać przepływ pracy i jakość.
Znaczenie jasnego określenia ról
3. Strategie tworzenia gałęzi i kontrola wersji
Zespoły korzystają z przepływów pracy Git, które obejmują gałęzie funkcjonalne, gałęzie krótkotrwałe oraz chronione gałęzie główne, aby izolować zmiany, umożliwiać pracę równoległą i zmniejszyć ryzyko konfliktów podczas scalania. Pull requesty zapewniają ustrukturyzowaną weryfikację oraz możliwość śledzenia zmian od pomysłu aż do scalenia.
Szukasz więcej informacji? Dowiedz się, jak Git wpisuje się w przepływy pracy Agile dla programistów w tym przydatnym artykule.
4. Ciągła integracja, testowanie i gotowość do wydania
Programiści przeprowadzają częste integracje. Każdy commit uruchamia zautomatyzowane kompilacje i testy. Pozwala to wcześnie wykrywać defekty, utrzymuje gotowość głównej gałęzi do wdrożenia i skraca pętle informacji zwrotnej.
Pipeline'y wydań automatyzują pakiety, promocję środowiska i weryfikację. Ale nic z tego nie jest możliwe bez wdrożenia najlepszych praktyk ciągłej integracji.
5. Dług techniczny i reakcja na incydenty jako najważniejsza praca
Zespoły Agile traktują odporność i łatwość konserwacji jako cechy produktu. Programiści planują refaktory, spłacają dług techniczny i stosują nienaganną reakcję na incydenty. Skraca to przyszły czas cyklu i zwiększa przekonanie do zmian.
5 najlepszych praktyk dla twórców oprogramowania w zakresie stosowania metodyki Agile
Każdy zespół ma własne unikalne podejście do Agile, ale istnieje kilka wskazówek, których warto przestrzegać, aby stosować tę metodologię płynniej i szybciej.
1. Zastosowanie przepływu pracy, w którym gałąź jest tworzona dla każdego zadania za pomocą metodycznych pull requestów
Dzięki solidnej strategii tworzenia gałęzi baza kodów pozostaje w dobrej kondycji, a zespół jest produktywny. Stwórz osobną gałąź dla każdej historyjki, każdego błędu lub krótkiego impulsu i utrzymuj krótkotrwałość gałęzi, aby uniknąć dryfowania kodu.
Użyj szablonów pull requestów, aby zapewnić kontekst, w tym zakres, zrzuty ekranu, testy i plany wdrażania. Zawsze wymagaj co najmniej jednej oceny przez współpracownika i upewnij się, że wszystkie kontrole CI zakończą się przed scaleniem.
Porada eksperta
2. Stworzenie solidnego zabezpieczenia dzięki zautomatyzowanym testom i ciągłej integracji
Solidne zabezpieczenie zaczyna się od zautomatyzowanych testów i ciągłej integracji. Dąż do zrównoważonej piramidy testowej: postaw na szybkie testy jednostkowe, dodaj ukierunkowane testy komponentów lub testy kontraktowe i zachowaj zgodne z zasadami lean i krótkie testy kompleksowe.
Przeprowadzaj wszystkie testy każdego commitu za pomocą ciągłej integracji, aby wcześnie wykrywać problemy, oraz skróć czas kompilacji, aby programiści pozostali produktywni. Zautomatyzuj analizę statyczną, skanowanie zabezpieczeń i linting, aby wykryć wady przed przeglądem kodu, dzięki czemu baza kodu jest bezpieczniejsza i bardziej niezawodna.
3. Określenie i uszanowanie „ukończenia”
Staranne zdefiniowanie ukończenia (DoD) powinno obejmować: wdrożony kod, dodane i zakończone powodzeniem testy, sprawdzony kod, kontrole bezpieczeństwa i jakości oznaczone na zielono, zaktualizowaną dokumentację oraz zdefiniowane przełączniki funkcji lub plan wdrożenia.
Zapewnij widoczność definicji ukończenia (DoD) w repozytorium lub projekcie i wykorzystaj automatyzację (obowiązkowe kontrole, zabezpieczenia gałęzi), aby egzekwować jej przestrzeganie w sposób spójny i konsekwentny.

4. Traktowanie długu technicznego jako elementu backlogu
Traktuj refaktory i dług techniczny jako najważniejsze elementy backlogu. To zapewni im jasne kryteria akceptacji i mierzalne wyniki, takie jak krótszy czas kompilacji lub mniej niespójnych testów.
W każdym sprincie przeznacz czas na konserwację, niezawodność i pracę nad wydajnością, używając budżetów błędów lub wskaźników operacyjnych do pomocy w nadaniu priorytetu temu, co najważniejsze.
5. Zamknięcie pętli dzięki danym — planowanie, mierzenie i uczenie się
Używaj umów zespołowych oraz celów sprintu, aby utrzymać zespół skoncentrowany na wynikach, które przynoszą realną wartość dla użytkowników i wywołują zauważalne zmiany w zachowaniu, a nie tylko na realizacji zadań. Śledź wskaźniki takie jak czas cyklu, prace w toku, wskaźnik niezauważonych wad, wskaźnik błędnych zmian oraz średni czas przywracania sprawności.
Pomoże to w prowadzeniu ciągłego doskonalenia oraz znaczących eksperymentów podczas retrospektyw w zespole programistycznym.

Integracja informacji dla zespołów programistycznych
Agile pomaga programistom dostarczać wartość na każdym etapie, jednocześnie zapewniając płynne działanie systemów. Operując na małych, przystępnych elementach oraz wcześnie testując i integrując, zespoły mogą przyspieszyć pracę.
Wspólne przeglądanie kodu i kontrolowanie na bieżąco długu technicznego pomaga wszystkim nabrać przekonania do każdej zmiany. Natomiast Jira pozwala jeszcze łatwiej śledzić postępy, szybko uzyskiwać informację zwrotną i sprawić, że wszyscy są na bieżąco.
Jaki jest tego efekt?
Lepsze oprogramowanie, bardziej zadowolone zespoły i swoboda wysyłania mniejszych partii, szybszego uczenia się i rozwiązywania problemów — to przewaga Agile dzięki Jirze.
Recommended for you
Szablony
Gotowe szablony Jira
Przejrzyj naszą bibliotekę niestandardowych szablonów Jira dla różnych zespołów, działów i przepływów pracy.
Przewodnik po produktach
Kompleksowe wprowadzenie do Jira
Skorzystaj z tego przewodnika krok po kroku, aby poznać podstawowe funkcje oraz najlepsze praktyki i pracować wydajniej.
Przewodnik po Git
Zrozumienie podstaw Git
Dla początkujących i zaawansowanych ekspertów — ten przewodnik po Git pomoże Ci opanować podstawy dzięki pomocnym samouczkom i poradom