O que é gerenciamento do fluxo de valor (VSM) e por que é importante?

Use o template grátis de mapeamento dos fluxos de valor
Key Takeaways
Value stream management (VSM) optimizes the flow of value from idea to customer, improving delivery speed and quality.
VSM connects business strategy with Agile and DevOps teams, breaking down silos and aligning around customer outcomes.
Mapping value streams reveals bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and opportunities for improvement.
Implement VSM to increase predictability, customer satisfaction, and innovation across your organization.
O que é gerenciamento do fluxo de valor (VSM) e por que é importante?
Software são diferenciais importantes em muitos setores. O tempo que as empresas levam para transformar solicitações do cliente em funções a serem entregues afeta o sucesso a longo prazo.
Empresas ágeis com produtos e serviços digitais que agradam os clientes conquistam fatias de mercado e aumentam a receita, enquanto empresas menos responsivas encontram dificuldades.
Para manter a competitividade, iniciativas de agilidade empresarial foram implementadas em empresas maiores. Nem todas essas iniciativas tiveram o sucesso esperado por vários motivos, incluindo resistência organizacional, liderança deficiente e falta de alinhamento. Como a incerteza econômica faz com que as empresas cortem pessoal e orçamentos, simplificar a entrega de produtos é ainda mais essencial. A gestão do fluxo de valor pode revitalizar os esforços de agilidade empresarial e proporcionar uma forma de satisfazer as necessidades dos clientes, oferecer resultados mais previsíveis e formas de adaptação às mudanças do mercado.
O que é gerenciamento de fluxo de valor (VSM)?
A gestão do fluxo de valor é o conjunto de práticas que melhoram a forma como as equipes oferecem experiências de alta qualidade aos clientes. A VSM prioriza duas coisas: a rapidez com que as funções ou atualizações solicitados pelo cliente são entregues e se o cliente percebe o valor dessas mudanças. De acordo com a Forrester, "a gestão do fluxo de valor (VSM) tem o potencial de transformar como um todo o processo de financiamento, construção, gerenciamento e manutenção de software em escala". As raízes da gestão do fluxo de valor estão na fabricação lean e se conectam ao Sistema Toyota de Produção (TPS) na década de 1950. Essa abordagem sistemática foi projetada para reduzir o tempo até valorização e fornecer produtos de maior qualidade. A gestão do fluxo de valor ajuda a conectar a diretoria às equipes ágeis e de DevOps para que haja alinhamento com a satisfação do cliente. A gestão dos fluxos de valor proporciona:
Entrega mais rápida de produtos centrados no cliente, aumentando a competitividade e a receita
Melhores experiências do cliente, gerando avaliações e referências positivas
Maior envolvimento dos funcionários com equipes multifuncionais, permitindo que as pessoas tenham uma visão geral, em vez de apenas do seu próprio silo
Tomada de decisões baseada em dados e insights para investimentos futuros
O que são fluxos de valor?
A Gartner define fluxo de valor como “a sequência de atividades necessárias para entregar um produto, serviço ou experiência a um cliente, interno ou externo”. Os fluxos de valor já existem nas empresas, mesmo que não tenham esse nome. Entender os fluxos de valor permite que você faça melhores decisões de investimento, evitando desperdício de recursos. Os fluxos de valor incluem todos os pontos de contato na jornada, desde a ideia original até a entrega de valor aos clientes. Sem esse conhecimento, você não vai saber o que está funcionando e o que tem problemas. Por exemplo, você pode encontrar longos atrasos durante as transferências entre equipes, o que prejudica a produtividade e a qualidade.
Fluxos de valor no desenvolvimento de software
Os fluxos de valor e o DevOps têm como base os princípios lean. Pensar e trabalhar como fluxos de valor ajudam as equipes de tecnologia a identificar e priorizar áreas de melhoria no desenvolvimento de software. O DevOps disponibiliza práticas e ferramentas para melhorar a entrega do fluxo de valor. Ao focar na otimização do fluxo, as ineficiências são identificadas e os processos são simplificados.
O que é mapeamento dos fluxos de valor?
O mapeamento dos fluxos de valor é uma técnica de colaboração visual usada para descrever fluxos de valor identificando e analisando o fluxo de atividades necessárias para entregar produtos ou serviços aos clientes. O mapeamento dos fluxos de valor revela dependências, obstáculos, ineficiências e desperdícios que comprometem os orçamentos e atrasam as entregas. Para mapear fluxos de valor, equipes multifuncionais coletam dados para identificar etapas e medir o tempo de atividade e inatividade de cada etapa. Esse processo permite que seja calculado o tempo de ciclo do fluxo de valor ao somar todos os tempos de atividade e de inatividade. Usando quadros brancos ou software de mapeamento para colaboração visual, as equipes podem designar se itens agregam ou não valor do ponto de vista do cliente. Eles também podem determinar áreas problemáticas, como equipes com falta de pessoal que impedem que outras avancem.
Por que o gerenciamento do fluxo de valor é importante?
Muitas vezes, o que clientes dizem que querem (com base em fontes como suporte ao cliente ou equipes de vendas) não é o que de fato está sendo entregue. A falta de comunicação eficaz entre as equipes de negócios e as de tecnologia é parte do problema. Embora a diretoria esteja focada em metas e estratégias gerais, os líderes de tecnologia se comunicam em termos de frequência de entrega e resultados técnicos. Os líderes e equipes precisam falar a mesma língua e estabelecer melhores canais de comunicação para se alinharem às metas e à experiência do cliente. A gestão do fluxo de valor viabiliza a comunicação entre equipes para melhorar o fluxo de informações e a criação de valor. O cliente solicita alguma função por meio das equipes de vendas ou suporte; depois, equipes de produto projetam as funcionalidades, as equipes de engenharia criam o software e depois o produto é enviado. Ter representantes de cada equipe em equipes multifuncionais torna a entrega do produto correto mais eficiente e eficaz. Os problemas abordados pela VSM incluem:
Frustração do cliente com as ofertas atuais
Correções lentas de bugs e demora em novas funções ou produtos
Perda de fatias do mercado para concorrentes que se adaptam com mais rapidez às mudanças no setor
Diminuição de recursos devido a demissões e outras medidas de contingenciamento
Transformações ágeis e/ou digitais não funcionam com a eficiência pretendida
Falta de visibilidade na empresa devido a silos e dados desiguais
Estrutura organizacional não projetada para criação de valor
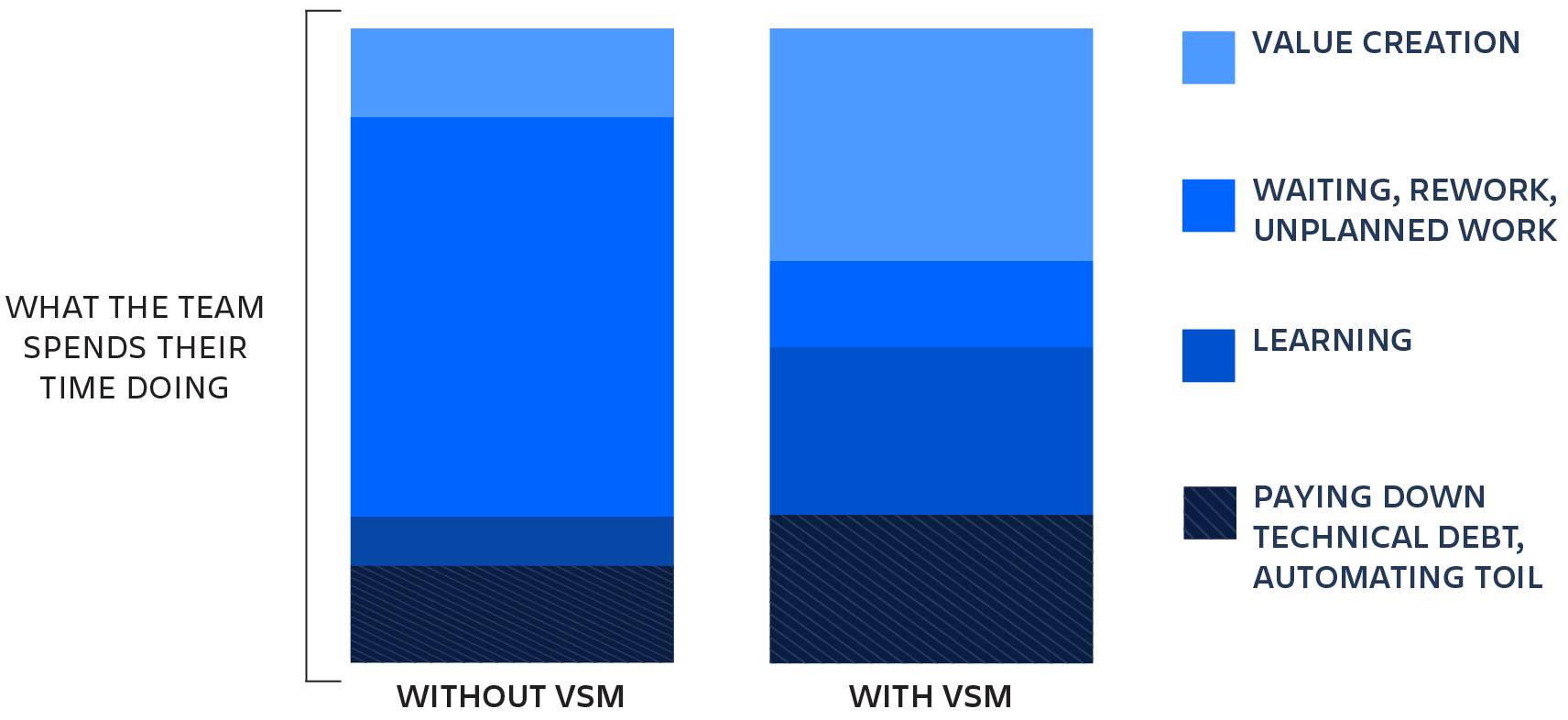
Quais são os benefícios do gerenciamento do fluxo de valor?
Depois que os fluxos de valor são identificados e mapeados, as empresas podem fazer análises para criar novos produtos ou funções. Eles podem usar insights atualizados e informados ao longo do fluxo de valor para melhorar a tomada de decisões, como o que os clientes pensam sobre os produtos atuais e o que precisa mudar. Em vez de investir em projetos individuais, todo o fluxo de valor pode ser financiado, dando flexibilidade para se adaptar às mudanças de necessidades dos clientes sem precisar de novas solicitações de orçamento. Os benefícios da gestão do fluxo de valor incluem:
Maior previsibilidade.
A compreensão de todo o fluxo de valor reduz a incerteza e as surpresas que levam à perda de prazos.
Maior satisfação do cliente.
Respostas rápidas às solicitações dos clientes podem melhorar a experiência deles e a reputação da empresa.
Melhor produtividade.
A simplificação das operações e a redução dos obstáculos permitem que as equipes idealizem, testem e entreguem com mais rapidez.
Custos reduzidos.
A identificação de trabalho desnecessário e recursos desperdiçados economiza tempo e dinheiro.
Software melhor.
A automatização de tarefas manuais libera tempo para inovação e reduz as chances de erros e defeitos.
Maior visibilidade de ponta a ponta.
Dados atualizados disponíveis por toda a empresa permitem que as pessoas acompanhem as iniciativas e se adaptem às mudanças nas prioridades corporativas.
Impulso em inovação e motivação.
Focar em produtos que importam de verdade para os clientes é mais satisfatório para os desenvolvedores.
Soluções de gerenciamento de fluxo de valor
As soluções de gestão do fluxo de valor ajudam os líderes a elevar o pensamento sobre o fluxo de valor em toda a empresa para aumentar a eficácia das equipes. As equipes precisam de acesso atualizado aos dados e relatórios para entender se os processos estão funcionando sem problemas. Ferramentas de VSM podem ser usadas para melhoria contínua e também para correlacionar os investimentos com o valor para o cliente. As soluções de software de VSM escalam a colaboração sem reduzir a velocidade das equipes ao:
Oferecer visão integrada que elimina os silos da empresa
Conectar pessoas, trabalho e tempo em todos os níveis da empresa
Combinar dados de fontes diferentes, como conjuntos de ferramentas heterogêneos
Criar uma fonte única de informações sem interromper as operações diárias
Reforçar com regularidade as melhores práticas ágeis
Trabalhar com a estrutura escolhida, como SAFe, Scrum@Scale, LeSS, Disciplined Agile, Spotify ou híbridos.
Entregar ferramentas para equipes em todos os níveis, desde executivos até release trains
Gerenciar com iniciativa as dependências entre equipes para melhorar a previsibilidade
Criar ambientes de melhoria contínua com ciclos de feedback reduzidos
Medir e analisar as coisas importantes
As soluções do VSM permitem que as equipes atuem com autonomia para entregar os produtos solicitados pelos clientes; depois, analisam se resultaram em mudanças tangíveis e mensuráveis nas experiências dos clientes e respondem ao que aprenderam.
Métricas do fluxo de valor para medir metas e progresso
Muitas empresas sofrem com a falta de visibilidade e relatórios abrangentes, sobretudo aquelas que são muito matriciais. As soluções de gerenciamento de fluxo de valor eliminam bolhas, reunindo dados diferentes para entregar as métricas que você precisa e insights acionáveis.
Métricas de fluxo
As métricas de fluxo avaliam a taxa de entrega de valor em relação aos resultados comerciais pretendidos.
Velocidade de fluxo
A velocidade do fluxo mede o número de unidades de valor que são concluídas durante um período específico dentro de um fluxo de valor.
Tempo de fluxo
O tempo de fluxo mede o tempo desde o início do trabalho em uma unidade de valor dentro de um fluxo de valor até o momento em que ele é lançado para um cliente. Tempos de fluxo excessivos podem indicar ineficiências ou gargalos.
Carga de fluxo
As medidas de carga de fluxo avaliam o trabalho em andamento (WIP), um indicador importante que se correlaciona com ineficiências dentro de um fluxo de valor.
Eficiência de fluxo
A eficiência do fluxo mede a proporção de tempo em que as unidades de valor são trabalhadas em comparação com o tempo total do fluxo. Uma baixa eficiência do fluxo pode indicar longos tempos de espera entre as etapas, causando grandes filas e mais WIP.
Distribuição de fluxo
A distribuição do fluxo mede a proporção dos itens de fluxo acima concluídos durante um período. É útil para definir prioridades necessárias visando atingir metas corporativas e da equipe.
Métricas DORA
As métricas DORA avaliam e melhoram a eficácia das equipes de DevOps.
Tempo de espera para mudanças
É o tempo decorrido entre o momento em que uma alteração de código é confirmada na ramificação principal e o momento em que ela está em estado de implantação.
Alterar taxa de falhas
É a porcentagem de alterações no código que exigem correções urgentes ou outras medidas corretivas após a produção.
Frequência de implementação
Mede a frequência com que novos códigos são implantados na produção e pode ser usada para medir a velocidade e a agilidade de uma equipe.
Tempo médio para recuperação (MTTR)
Mede o tempo necessário para recuperar de uma interrupção parcial do serviço ou de uma falha total.
Objetivos e principais resultados (OKRs)
As empresas precisam manter o trabalho das equipes alinhado às metas corporativas. Os objetivos e resultados-chave (OKRs) têm dois componentes: o objetivo que você quer alcançar e os principais resultados que medem o sucesso. Os diretores definem OKRs de alto nível conectados com a missão, visão e valores fundamentais da empresa. Equipes individuais decidem como atingir essas metas definindo seus próprios OKRs em nível de equipe. Os OKRs podem ser definidos a cada trimestre para facilitar as tomadas de decisão entre mudar ou persistir com base em novos dados ou alterações no mercado. Eles também são rastreados para que você possa ver o status atual das atividades, estejam elas no horário, em risco ou bloqueadas.
Como o VSM melhora a realização de valor?
A realização de valor se concentra em garantir que os itens certos sejam trabalhados, entreguem o que prometem e contribuam para o próximo ciclo de desenvolvimento de produtos. Embora se dê prioridade ao desenvolvimento de novos produtos ou funções em vez de melhorias sistêmicas, é necessária uma visão holística ao fazer investimentos em funções, defeitos, dívida técnica e risco. A realização de valor pode ser dividida em duas categorias:
Produção (integridade do fluxo de valor)
A produção está conectada ao fluxo de trabalho, da ideia à realização e à entrega do fluxo contínuo de valor para os clientes. Melhorar o sistema de entrega subjacente (pessoas, processos e tecnologia) libera mais tempo para a criação de valor. Ao medir a distribuição do trabalho e os tempos de ciclo, as equipes podem ver como suas ações afetam a capacidade de oferecer novas funções e aumentar a capacidade.
Resultados (experiências do cliente)
Ao medir a experiência do cliente, as equipes podem ver se entregaram o valor que o cliente queria, com base em indicadores como maior uso por parte do cliente ou avaliações positivas. Essas métricas (com base em dados, feedback e análise) dão às equipes as informações necessárias para tomar decisões e investimentos futuros.
O que é gerenciamento do fluxo de valor (VSM) e por que é importante?

Use o template grátis de mapeamento dos fluxos de valor
Key Takeaways
Value stream management (VSM) optimizes the flow of value from idea to customer, improving delivery speed and quality.
VSM connects business strategy with Agile and DevOps teams, breaking down silos and aligning around customer outcomes.
Mapping value streams reveals bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and opportunities for improvement.
Implement VSM to increase predictability, customer satisfaction, and innovation across your organization.
O que é gerenciamento do fluxo de valor (VSM) e por que é importante?
Software são diferenciais importantes em muitos setores. O tempo que as empresas levam para transformar solicitações do cliente em funções a serem entregues afeta o sucesso a longo prazo.
Empresas ágeis com produtos e serviços digitais que agradam os clientes conquistam fatias de mercado e aumentam a receita, enquanto empresas menos responsivas encontram dificuldades.
Para manter a competitividade, iniciativas de agilidade empresarial foram implementadas em empresas maiores. Nem todas essas iniciativas tiveram o sucesso esperado por vários motivos, incluindo resistência organizacional, liderança deficiente e falta de alinhamento. Como a incerteza econômica faz com que as empresas cortem pessoal e orçamentos, simplificar a entrega de produtos é ainda mais essencial. A gestão do fluxo de valor pode revitalizar os esforços de agilidade empresarial e proporcionar uma forma de satisfazer as necessidades dos clientes, oferecer resultados mais previsíveis e formas de adaptação às mudanças do mercado.
O que é gerenciamento de fluxo de valor (VSM)?
A gestão do fluxo de valor é o conjunto de práticas que melhoram a forma como as equipes oferecem experiências de alta qualidade aos clientes. A VSM prioriza duas coisas: a rapidez com que as funções ou atualizações solicitados pelo cliente são entregues e se o cliente percebe o valor dessas mudanças. De acordo com a Forrester, "a gestão do fluxo de valor (VSM) tem o potencial de transformar como um todo o processo de financiamento, construção, gerenciamento e manutenção de software em escala". As raízes da gestão do fluxo de valor estão na fabricação lean e se conectam ao Sistema Toyota de Produção (TPS) na década de 1950. Essa abordagem sistemática foi projetada para reduzir o tempo até valorização e fornecer produtos de maior qualidade. A gestão do fluxo de valor ajuda a conectar a diretoria às equipes ágeis e de DevOps para que haja alinhamento com a satisfação do cliente. A gestão dos fluxos de valor proporciona:
Entrega mais rápida de produtos centrados no cliente, aumentando a competitividade e a receita
Melhores experiências do cliente, gerando avaliações e referências positivas
Maior envolvimento dos funcionários com equipes multifuncionais, permitindo que as pessoas tenham uma visão geral, em vez de apenas do seu próprio silo
Tomada de decisões baseada em dados e insights para investimentos futuros
O que são fluxos de valor?
A Gartner define fluxo de valor como “a sequência de atividades necessárias para entregar um produto, serviço ou experiência a um cliente, interno ou externo”. Os fluxos de valor já existem nas empresas, mesmo que não tenham esse nome. Entender os fluxos de valor permite que você faça melhores decisões de investimento, evitando desperdício de recursos. Os fluxos de valor incluem todos os pontos de contato na jornada, desde a ideia original até a entrega de valor aos clientes. Sem esse conhecimento, você não vai saber o que está funcionando e o que tem problemas. Por exemplo, você pode encontrar longos atrasos durante as transferências entre equipes, o que prejudica a produtividade e a qualidade.
Fluxos de valor no desenvolvimento de software
Os fluxos de valor e o DevOps têm como base os princípios lean. Pensar e trabalhar como fluxos de valor ajudam as equipes de tecnologia a identificar e priorizar áreas de melhoria no desenvolvimento de software. O DevOps disponibiliza práticas e ferramentas para melhorar a entrega do fluxo de valor. Ao focar na otimização do fluxo, as ineficiências são identificadas e os processos são simplificados.
O que é mapeamento dos fluxos de valor?
O mapeamento dos fluxos de valor é uma técnica de colaboração visual usada para descrever fluxos de valor identificando e analisando o fluxo de atividades necessárias para entregar produtos ou serviços aos clientes. O mapeamento dos fluxos de valor revela dependências, obstáculos, ineficiências e desperdícios que comprometem os orçamentos e atrasam as entregas. Para mapear fluxos de valor, equipes multifuncionais coletam dados para identificar etapas e medir o tempo de atividade e inatividade de cada etapa. Esse processo permite que seja calculado o tempo de ciclo do fluxo de valor ao somar todos os tempos de atividade e de inatividade. Usando quadros brancos ou software de mapeamento para colaboração visual, as equipes podem designar se itens agregam ou não valor do ponto de vista do cliente. Eles também podem determinar áreas problemáticas, como equipes com falta de pessoal que impedem que outras avancem.
Por que o gerenciamento do fluxo de valor é importante?
Muitas vezes, o que clientes dizem que querem (com base em fontes como suporte ao cliente ou equipes de vendas) não é o que de fato está sendo entregue. A falta de comunicação eficaz entre as equipes de negócios e as de tecnologia é parte do problema. Embora a diretoria esteja focada em metas e estratégias gerais, os líderes de tecnologia se comunicam em termos de frequência de entrega e resultados técnicos. Os líderes e equipes precisam falar a mesma língua e estabelecer melhores canais de comunicação para se alinharem às metas e à experiência do cliente. A gestão do fluxo de valor viabiliza a comunicação entre equipes para melhorar o fluxo de informações e a criação de valor. O cliente solicita alguma função por meio das equipes de vendas ou suporte; depois, equipes de produto projetam as funcionalidades, as equipes de engenharia criam o software e depois o produto é enviado. Ter representantes de cada equipe em equipes multifuncionais torna a entrega do produto correto mais eficiente e eficaz. Os problemas abordados pela VSM incluem:
Frustração do cliente com as ofertas atuais
Correções lentas de bugs e demora em novas funções ou produtos
Perda de fatias do mercado para concorrentes que se adaptam com mais rapidez às mudanças no setor
Diminuição de recursos devido a demissões e outras medidas de contingenciamento
Transformações ágeis e/ou digitais não funcionam com a eficiência pretendida
Falta de visibilidade na empresa devido a silos e dados desiguais
Estrutura organizacional não projetada para criação de valor

Quais são os benefícios do gerenciamento do fluxo de valor?
Depois que os fluxos de valor são identificados e mapeados, as empresas podem fazer análises para criar novos produtos ou funções. Eles podem usar insights atualizados e informados ao longo do fluxo de valor para melhorar a tomada de decisões, como o que os clientes pensam sobre os produtos atuais e o que precisa mudar. Em vez de investir em projetos individuais, todo o fluxo de valor pode ser financiado, dando flexibilidade para se adaptar às mudanças de necessidades dos clientes sem precisar de novas solicitações de orçamento. Os benefícios da gestão do fluxo de valor incluem:
Maior previsibilidade.
A compreensão de todo o fluxo de valor reduz a incerteza e as surpresas que levam à perda de prazos.
Maior satisfação do cliente.
Respostas rápidas às solicitações dos clientes podem melhorar a experiência deles e a reputação da empresa.
Melhor produtividade.
A simplificação das operações e a redução dos obstáculos permitem que as equipes idealizem, testem e entreguem com mais rapidez.
Custos reduzidos.
A identificação de trabalho desnecessário e recursos desperdiçados economiza tempo e dinheiro.
Software melhor.
A automatização de tarefas manuais libera tempo para inovação e reduz as chances de erros e defeitos.
Maior visibilidade de ponta a ponta.
Dados atualizados disponíveis por toda a empresa permitem que as pessoas acompanhem as iniciativas e se adaptem às mudanças nas prioridades corporativas.
Impulso em inovação e motivação.
Focar em produtos que importam de verdade para os clientes é mais satisfatório para os desenvolvedores.
Soluções de gerenciamento de fluxo de valor
As soluções de gestão do fluxo de valor ajudam os líderes a elevar o pensamento sobre o fluxo de valor em toda a empresa para aumentar a eficácia das equipes. As equipes precisam de acesso atualizado aos dados e relatórios para entender se os processos estão funcionando sem problemas. Ferramentas de VSM podem ser usadas para melhoria contínua e também para correlacionar os investimentos com o valor para o cliente. As soluções de software de VSM escalam a colaboração sem reduzir a velocidade das equipes ao:
Oferecer visão integrada que elimina os silos da empresa
Conectar pessoas, trabalho e tempo em todos os níveis da empresa
Combinar dados de fontes diferentes, como conjuntos de ferramentas heterogêneos
Criar uma fonte única de informações sem interromper as operações diárias
Reforçar com regularidade as melhores práticas ágeis
Trabalhar com a estrutura escolhida, como SAFe, Scrum@Scale, LeSS, Disciplined Agile, Spotify ou híbridos.
Entregar ferramentas para equipes em todos os níveis, desde executivos até release trains
Gerenciar com iniciativa as dependências entre equipes para melhorar a previsibilidade
Criar ambientes de melhoria contínua com ciclos de feedback reduzidos
Medir e analisar as coisas importantes
As soluções do VSM permitem que as equipes atuem com autonomia para entregar os produtos solicitados pelos clientes; depois, analisam se resultaram em mudanças tangíveis e mensuráveis nas experiências dos clientes e respondem ao que aprenderam.
Métricas do fluxo de valor para medir metas e progresso
Muitas empresas sofrem com a falta de visibilidade e relatórios abrangentes, sobretudo aquelas que são muito matriciais. As soluções de gerenciamento de fluxo de valor eliminam bolhas, reunindo dados diferentes para entregar as métricas que você precisa e insights acionáveis.
Métricas de fluxo
As métricas de fluxo avaliam a taxa de entrega de valor em relação aos resultados comerciais pretendidos.
Velocidade de fluxo
A velocidade do fluxo mede o número de unidades de valor que são concluídas durante um período específico dentro de um fluxo de valor.
Tempo de fluxo
O tempo de fluxo mede o tempo desde o início do trabalho em uma unidade de valor dentro de um fluxo de valor até o momento em que ele é lançado para um cliente. Tempos de fluxo excessivos podem indicar ineficiências ou gargalos.
Carga de fluxo
As medidas de carga de fluxo avaliam o trabalho em andamento (WIP), um indicador importante que se correlaciona com ineficiências dentro de um fluxo de valor.
Eficiência de fluxo
A eficiência do fluxo mede a proporção de tempo em que as unidades de valor são trabalhadas em comparação com o tempo total do fluxo. Uma baixa eficiência do fluxo pode indicar longos tempos de espera entre as etapas, causando grandes filas e mais WIP.
Distribuição de fluxo
A distribuição do fluxo mede a proporção dos itens de fluxo acima concluídos durante um período. É útil para definir prioridades necessárias visando atingir metas corporativas e da equipe.
Métricas DORA
As métricas DORA avaliam e melhoram a eficácia das equipes de DevOps.
Tempo de espera para mudanças
É o tempo decorrido entre o momento em que uma alteração de código é confirmada na ramificação principal e o momento em que ela está em estado de implantação.
Alterar taxa de falhas
É a porcentagem de alterações no código que exigem correções urgentes ou outras medidas corretivas após a produção.
Frequência de implementação
Mede a frequência com que novos códigos são implantados na produção e pode ser usada para medir a velocidade e a agilidade de uma equipe.
Tempo médio para recuperação (MTTR)
Mede o tempo necessário para recuperar de uma interrupção parcial do serviço ou de uma falha total.
Objetivos e principais resultados (OKRs)
As empresas precisam manter o trabalho das equipes alinhado às metas corporativas. Os objetivos e resultados-chave (OKRs) têm dois componentes: o objetivo que você quer alcançar e os principais resultados que medem o sucesso. Os diretores definem OKRs de alto nível conectados com a missão, visão e valores fundamentais da empresa. Equipes individuais decidem como atingir essas metas definindo seus próprios OKRs em nível de equipe. Os OKRs podem ser definidos a cada trimestre para facilitar as tomadas de decisão entre mudar ou persistir com base em novos dados ou alterações no mercado. Eles também são rastreados para que você possa ver o status atual das atividades, estejam elas no horário, em risco ou bloqueadas.
Como o VSM melhora a realização de valor?
A realização de valor se concentra em garantir que os itens certos sejam trabalhados, entreguem o que prometem e contribuam para o próximo ciclo de desenvolvimento de produtos. Embora se dê prioridade ao desenvolvimento de novos produtos ou funções em vez de melhorias sistêmicas, é necessária uma visão holística ao fazer investimentos em funções, defeitos, dívida técnica e risco. A realização de valor pode ser dividida em duas categorias:
Produção (integridade do fluxo de valor)
A produção está conectada ao fluxo de trabalho, da ideia à realização e à entrega do fluxo contínuo de valor para os clientes. Melhorar o sistema de entrega subjacente (pessoas, processos e tecnologia) libera mais tempo para a criação de valor. Ao medir a distribuição do trabalho e os tempos de ciclo, as equipes podem ver como suas ações afetam a capacidade de oferecer novas funções e aumentar a capacidade.
Resultados (experiências do cliente)
Ao medir a experiência do cliente, as equipes podem ver se entregaram o valor que o cliente queria, com base em indicadores como maior uso por parte do cliente ou avaliações positivas. Essas métricas (com base em dados, feedback e análise) dão às equipes as informações necessárias para tomar decisões e investimentos futuros.
Templates
Templates prontos do Jira
Confira nossa biblioteca de templates personalizados do Jira para várias equipes, departamentos e fluxos de trabalho.
Guia do produto
Uma introdução completa ao Jira
Use este guia detalhado para descobrir as principais funções e as melhores práticas para maximizar sua produtividade.
Guia do Git
Como entender o básico do Git
De iniciantes a especialistas avançados, use este guia para aprender o básico do Git com dicas e tutoriais úteis.