Wat is het beheer van waardestromen (VSM) en waarom is het belangrijk?

Gratis sjabloon voor waardestroommapping gebruiken
Key Takeaways
Value stream management (VSM) optimizes the flow of value from idea to customer, improving delivery speed and quality.
VSM connects business strategy with Agile and DevOps teams, breaking down silos and aligning around customer outcomes.
Mapping value streams reveals bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and opportunities for improvement.
Implement VSM to increase predictability, customer satisfaction, and innovation across your organization.
Wat is het beheer van waardestromen (VSM) en waarom is het belangrijk?
Software is een belangrijke onderscheidende factor in veel sectoren. De tijd die een bedrijf nodig heeft om een aanvraag van een klant om te zetten in een leverbare functie, is van invloed op het succes op lange termijn.
Behendige bedrijven met digitale producten en services waar klanten blij van worden, veroveren marktaandeel en verhogen hun omzet. Bedrijven die minder snel reageren, hebben het moeilijk.
Om concurrerend te blijven, zijn initiatieven op het gebied van bedrijfsflexibiliteit geïmplementeerd in grotere organisaties. Niet al deze initiatieven waren vanwege verschillende redenen zo succesvol als gehoopt, waaronder weerstand in de organisatie, slecht leiderschap en gebrek aan afstemming. Aangezien bedrijven bezuinigen op personeel en budgetten vanwege economische onzekerheid, is het stroomlijnen van de levering van producten nog belangrijker. Het beheer van waardestromen kan de inspanningen van bedrijven op het gebied van flexibiliteit nieuw leven inblazen en een manier bieden om aan de behoeften van klanten te voldoen, zich aan te passen aan marktveranderingen en voorspelbaarder te leveren.
Wat is het beheer van waardestromen (VSM)?
Het beheer van waardestromen (VSM) is een reeks praktijken die de manier verbeteren waarop teams hoogwaardige klantervaringen leveren. VSM richt zich op twee dingen: hoe snel de door de klant gevraagde functies of updates worden geleverd en of de klant de waarde van die wijzigingen realiseert. Volgens Forrester heeft "Het beheer van waardestromen (VSM) het potentieel om het proces van het financieren, bouwen, beheren en onderhouden van software volledig op grote schaal te transformeren." De wortels van het beheer van waardestromen liggen in lean manufacturing en sluiten aan op het Toyota Production System (TPS) uit de jaren vijftig. Deze systematische aanpak is bedoeld om een sneller rendement mogelijk te maken en producten van hogere kwaliteit te leveren. Het beheer van waardestromen helpt de C-suite in contact te brengen met Agile- en DevOps-teams om op elkaar af te stemmen voor klanttevredenheid. Het beheren van waardestromen biedt:
Snellere levering van klantgerichte producten, waardoor het concurrentievermogen wordt verhoogd en de inkomsten toenemen
Betere klantervaringen, wat leidt tot positieve beoordelingen en doorverwijzingen
Betere betrokkenheid van werknemers bij cross-functionele teams, waardoor mensen het grote geheel kunnen zien in plaats van alleen hun silo
Besluitvorming op basis van gegevens en inzichten voor toekomstige investeringen
Wat is een waardestroom?
Gartner definieert een waardestroom als 'de reeks activiteiten die nodig zijn om een product, service of ervaring te leveren aan een klant: intern of extern.' Waardestromen bestaan al in bedrijven, zelfs als ze niet als zodanig zijn gelabeld. Als je je waardestromen begrijpt, kun je betere investeringsbeslissingen nemen, zodat er geen middelen worden verspild. Waardestromen omvatten elk contactpunt op het traject, van het genereren van ideeën tot het leveren van waarde aan klanten. Zonder deze kennis weet je niet wat werkt en waar je problemen hebt. Je kunt bijvoorbeeld te maken krijgen met langdurige vertragingen tijdens overdrachten tussen teams, wat de productiviteit en kwaliteit negatief beïnvloedt.
Waardestromen in softwareontwikkeling
Waardestromen en DevOps zijn beide gebaseerd in de principes van lean. Denken en werken als waardestromen helpen technologieteams bij het identificeren en prioriteren van verbeterpunten op het gebied van softwareontwikkeling. DevOps biedt praktijken en tools om de levering van waardestromen te verbeteren. Door te focussen op stroomoptimalisatie, worden inefficiënties geïdentificeerd en worden processen gestroomlijnd.
Wat is waardestroommapping?
Waardestroommapping is een visuele samenwerkingstechniek die wordt gebruikt om waardestromen te beschrijven door de stroom van activiteiten te identificeren en te analyseren die nodig is om een product of service aan een klant te leveren. Waardestroommapping brengt afhankelijkheden, blokkades, inefficiënties en verspilling aan het licht, waardoor budgetten worden overschreden en de levering wordt vertraagd. Om waardestromen in kaart te brengen, verzamelen cross-functionele teams gegevens om de stappen te identificeren en de actieve tijd en inactieve tijd voor elke stap te meten. Hierdoor kunnen teams de cyclustijd berekenen voor de waardestroom door alle actieve en inactieve tijden bij elkaar op te tellen. Door whiteboards of mappingsoftware te gebruiken om visueel samen te werken, kunnen teams items aanwijzen als items die waarde toevoegen of geen waarde toevoegen vanuit het perspectief van de klant. Ze kunnen ook probleemgebieden bepalen, zoals een team met te weinig personeel dat andere teams vertraagt om verder te werken.
Waarom is het beheer van waardestromen belangrijk?
Er is vaak een verschil tussen wat klanten zeggen dat ze willen (verkregen uit bronnen zoals klantenservice of salesteams) en wat er daadwerkelijk wordt geleverd. Het gebrek aan effectieve communicatie tussen bedrijfsteams en technologieteams is een onderdeel van het probleem. Hoewel de C-suite zich richt op doelen en algemene strategieën, spreken technologieleiders vaak in termen van leveringsfrequentie en technische outputs. Leiders en hun teams moeten een gemeenschappelijke taal en betere communicatiekanalen ontwikkelen om de doelstellingen en ervaringen van klanten op elkaar af te stemmen. Het beheer van waardestromen vergemakkelijkt communicatie tussen teams om de informatiestroom en waardecreatie te verbeteren. De klant vraagt een functie aan via sales- of supportteams, productteams ontwerpen de functionaliteit, technische teams bouwen de software en het product wordt geleverd. Met een vertegenwoordiger van elk team in een cross-functioneel team kan het juiste product efficiënter en effectiever worden geleverd. De problemen die door VSM worden aangepakt, zijn onder andere:
Frustratie van klanten over het huidige aanbod
Trage levering van bugfixes en nieuwe functies of producten
Marktaandeel verliezen aan concurrenten die zich snel aanpassen aan marktveranderingen
Minder middelen als gevolg van ontslagen werknemers en andere kostenbesparende maatregelen
Agile en/of digitale transformaties leveren niet zo effectief als gewenst
Gebrek aan zichtbaarheid in de hele organisatie als gevolg van silo's en uiteenlopende gegevens
Organisatiestructuur die niet is ontworpen voor waardecreatie
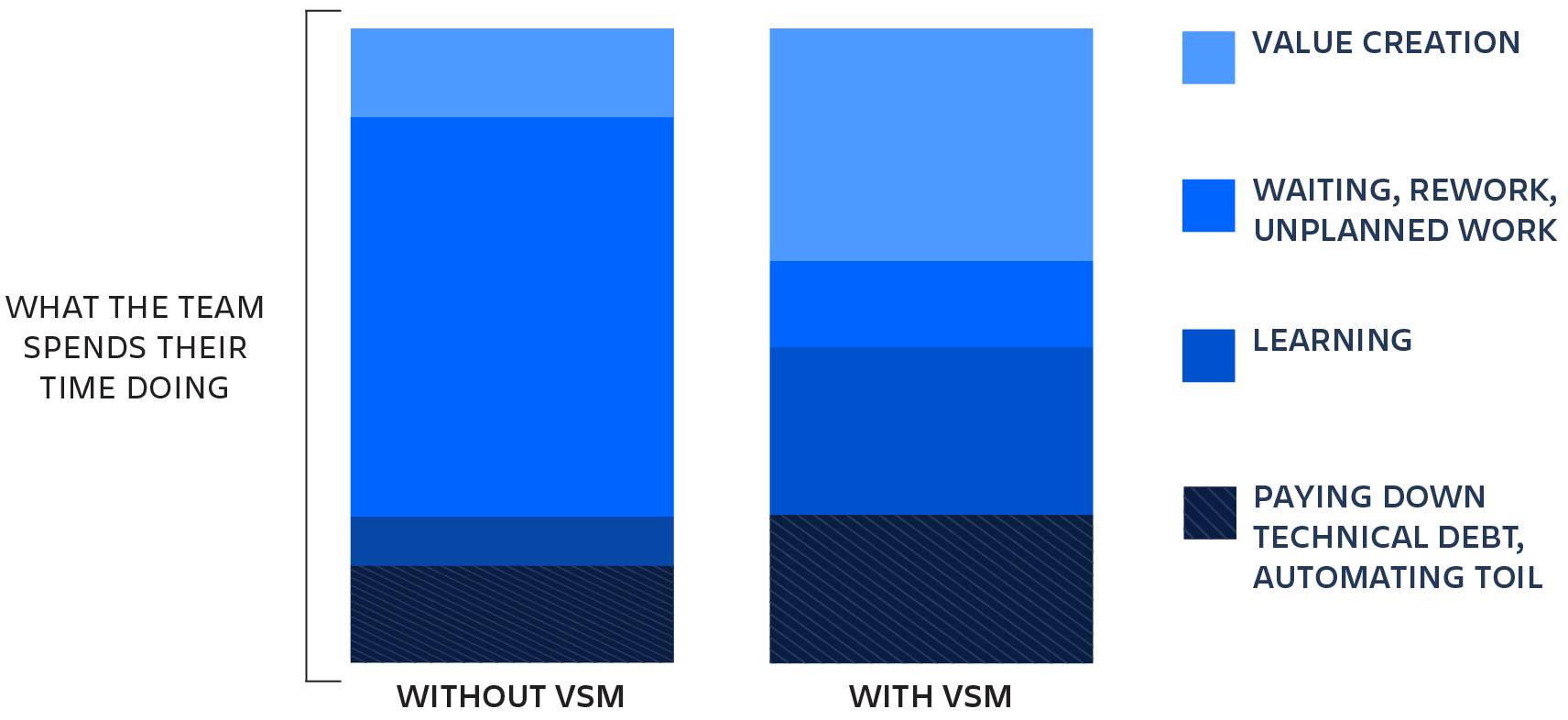
Wat zijn de voordelen van het beheer van waardestromen?
Zodra waardestromen zijn geïdentificeerd en toegewezen, kunnen bedrijven deze analyseren om nieuwe producten of functies aan te maken. Ze kunnen realtime, datagestuurde inzichten in de waardestroom gebruiken om betere zakelijke beslissingen te nemen, zoals wat klanten van huidige producten vinden en wat er moet veranderen. In plaats van te investeren in individuele projecten, kan de volledige waardestroom worden gefinancierd, wat flexibiliteit biedt om zich aan te passen aan veranderende behoeften van klanten zonder dat er nieuwe budgetaanvragen nodig zijn. De voordelen van het beheer van waardestromen zijn onder andere:
Toegenomen voorspelbaarheid.
Inzicht in de volledige waardestroom helpt om onzekerheid en verrassingen te verminderen die tot gemiste deadlines leiden.
Hogere klanttevredenheid.
Snel reageren op aanvragen van klanten kan hun ervaring en de reputatie van het bedrijf verbeteren.
Verbeterde productiviteit.
Door activiteiten te stroomlijnen en blokkades te verminderen, kunnen teams sneller ideeën bedenken, testen en leveren.
Lagere kosten.
Het identificeren van onnodig werk en verspilde middelen bespaart geld en tijd.
Betere software.
Door handmatige taken te automatiseren, komt er tijd vrij voor innovatie en wordt de kans op fouten en defecten verkleind.
Verbeterde zichtbaarheid van begin tot eind.
Omdat er in de hele organisatie realtime gegevens beschikbaar zijn, kunnen mensen initiatieven volgen en zich aanpassen aan veranderende bedrijfsprioriteiten.
Meer innovatie en beter moreel.
Ontwikkelaars vinden het fijner als ze zich kunnen richten op producten die echt belangrijk zijn voor klanten.
Oplossingen voor het beheer van waardestromen
Oplossingen voor het beheer van waardestromen helpen leiders om waardestroomdenken in de hele organisatie naar een hoger niveau te tillen om de effectiviteit van hun teams te vergroten. Teams hebben realtime toegang nodig tot gegevens en rapporten om te begrijpen of processen soepel verlopen. Ze kunnen de tools van VSM gebruiken om continue verbetering te stimuleren en investeringen te correleren aan de waarde van de klant. Softwareoplossingen van VSM vergroten de samenwerking zonder teams te vertragen door:
Het bieden van een geïntegreerde visie die bedrijfssilo's doorbreekt
Mensen, werk en tijd op elk niveau van het bedrijf te koppelen
Gegevens te combineren uit verschillende bronnen, zoals heterogene toolchains
Een enkele bron van waarheid aanmaken zonder de dagelijkse gang van zaken te verstoren
Voortdurende versterking van de best practices op het gebied van Agile
We werken met jouw gewenste framework, zoals SAFe, Scrum @Scale, LeSS, Disciplined Agile, Spotify of hybrides.
We bieden tools voor teams op elk niveau, van leidinggevenden tot releaseketens
Proactief omgaan met afhankelijkheden tussen teams om de voorspelbaarheid te verbeteren
Een omgeving aanmaken waarin voortdurend wordt verbeterd met kortere feedbackloops
Meten en analyseren van de dingen die er toe doen
Met oplossingen van VSM kunnen teams autonoom handelen om door klanten gevraagde producten te leveren, vervolgens te analyseren of deze hebben geleid tot tastbare, meetbare veranderingen in de klantervaringen, en te reageren op wat ze leren.
Statistieken van waardestromen voor het meten van doelen en voortgang
Veel bedrijven hebben te kampen met een gebrek aan zichtbaarheid en uitgebreide rapporten, vooral bedrijven die sterk op elkaar zijn afgestemd. Oplossingen voor waardestroombeheer doorkruisen silo's en brengen uiteenlopende gegevens samen om je de statistieken te geven die je nodig hebt en bruikbare inzichten.
Stroomstatistieken
Stroomstatistieken evalueren de mate van waardelevering in relatie tot de gewenste bedrijfsresultaten.
Stroomsnelheid
meet het aantal waarde-eenheden dat gedurende een bepaalde periode binnen een waardestroom is voltooid.
Stroomtijd
meet de tijd vanaf het moment dat wordt begonnen met werk aan een eenheid van waarde binnen een waardestroom tot het moment dat deze aan een klant wordt vrijgegeven. Te lange doorlooptijden kunnen wijzen op inefficiënties of knelpunten.
Stroombelasting
meet het werk in uitvoering (WIP), een belangrijke indicator die verband houdt met inefficiënties binnen een waardestroom.
Stroomefficiëntie
meet het aandeel van de tijd waaraan waardeeenheden actief worden gewerkt in vergelijking met de totale stroomtijd. Een lage stroomefficiëntie kan duiden op lange wachttijden tussen de stappen, wat leidt tot grote wachtrijen en meer WIP.
Stroomverdeling
meet de verhouding tussen de bovenstaande stroomitems die in een bepaalde periode zijn voltooid. Het is nuttig om prioriteit te geven aan het werk dat nodig is om bedrijfs- en teamdoelen te bereiken.
DORA-statistieken
DORA-statistieken evalueren en verbeteren de effectiviteit van DevOps-teams.
Doorlooptijd voor wijzigingen
betreft de tijdsduur tussen het moment dat een codewijziging wordt vastgelegd in de trunkbranch en wanneer deze geïmplementeerd kan worden.
Foutpercentage van wijzigingen
is het percentage codewijzigingen waarvoor hot fixes of andere hersteloplossingen na productie nodig zijn.
Implementatiefrequentie
meet hoe vaak nieuwe code wordt geïmplementeerd in de productie en kan worden gebruikt om de snelheid en flexibiliteit van een team te meten.
Gemiddelde tijd tot herstel (MTTR, Mean Time to Recovery)
meet hoelang de oplossing van een gedeeltelijke serviceonderbreking of totale storing duurt.
Doelstellingen en belangrijke resultaten (Objectives en Key Results of OKR's)
Ondernemingen moeten ervoor zorgen dat teams hun werk doen in lijn met de doelstellingen van het bedrijf. Doelstellingen en belangrijkste resultaten (OKR's) bestaan uit twee componenten: het doel dat je wilt bereiken en de belangrijkste resultaten die je succes meten. De C-suite stelt OKR's op hoog niveau vast die verband houden met de missie, visie en kernwaarden van de organisatie. Individuele teams beslissen hoe ze die doelen bereiken door hun eigen OKR's op teamniveau te stellen. OKR's kunnen op kwartaalbasis worden ingesteld, zodat beslissingen sneller kunnen worden aangepast of doorgezet op basis van nieuwe gegevens of marktveranderingen. OKR's worden bijgehouden zodat je de huidige status van activiteiten kunt zien, zoals of ze op tijd zijn, risico lopen of geblokkeerd zijn.
Hoe verbetert VSM de waardecreatie?
Waardecreatie is erop gericht om ervoor te zorgen dat er aan de juiste items wordt gewerkt, dat de items leveren wat de bedoeling is en dat ze bijdragen aan de volgende cyclus van productontwikkeling. Hoewel er meestal prioriteit wordt gegeven aan de ontwikkeling van nieuwe producten of functies in plaats van systemische verbeteringen, is een holistische kijk vereist bij investeringen in functies, defecten, technische schulden en risico's.Waardecreatie kan worden opgedeeld in twee categorieën:
Outputs (gezondheid van waardestromen)
Outputs zijn gekoppeld aan de werkstroom van idee tot realisatie en levering van een continue stroom van waarde voor klanten. Door verbeteringen aan te brengen in het onderliggende leveringssysteem (mensen, processen en technologie) komt er meer tijd vrij voor waardecreatie. Door de werkverdeling en cyclustijden te meten, kunnen teams zien welke invloed hun acties hebben op hun vermogen om nieuwe functies aan te bieden en de capaciteit te verhogen.
Resultaten (klantervaringen)
Door de klantervaring te meten, kunnen teams zien of ze de gewenste klantwaarde hebben geleverd, zoals een verhoogd aantal klanten of positieve beoordelingen. Deze statistieken (gebaseerd op gegevens, feedback en analyses) geven teams de informatie die nodig is om toekomstige beslissingen te nemen en investeringen te maken.
Wat is het beheer van waardestromen (VSM) en waarom is het belangrijk?

Gratis sjabloon voor waardestroommapping gebruiken
Key Takeaways
Value stream management (VSM) optimizes the flow of value from idea to customer, improving delivery speed and quality.
VSM connects business strategy with Agile and DevOps teams, breaking down silos and aligning around customer outcomes.
Mapping value streams reveals bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and opportunities for improvement.
Implement VSM to increase predictability, customer satisfaction, and innovation across your organization.
Wat is het beheer van waardestromen (VSM) en waarom is het belangrijk?
Software is een belangrijke onderscheidende factor in veel sectoren. De tijd die een bedrijf nodig heeft om een aanvraag van een klant om te zetten in een leverbare functie, is van invloed op het succes op lange termijn.
Behendige bedrijven met digitale producten en services waar klanten blij van worden, veroveren marktaandeel en verhogen hun omzet. Bedrijven die minder snel reageren, hebben het moeilijk.
Om concurrerend te blijven, zijn initiatieven op het gebied van bedrijfsflexibiliteit geïmplementeerd in grotere organisaties. Niet al deze initiatieven waren vanwege verschillende redenen zo succesvol als gehoopt, waaronder weerstand in de organisatie, slecht leiderschap en gebrek aan afstemming. Aangezien bedrijven bezuinigen op personeel en budgetten vanwege economische onzekerheid, is het stroomlijnen van de levering van producten nog belangrijker. Het beheer van waardestromen kan de inspanningen van bedrijven op het gebied van flexibiliteit nieuw leven inblazen en een manier bieden om aan de behoeften van klanten te voldoen, zich aan te passen aan marktveranderingen en voorspelbaarder te leveren.
Wat is het beheer van waardestromen (VSM)?
Het beheer van waardestromen (VSM) is een reeks praktijken die de manier verbeteren waarop teams hoogwaardige klantervaringen leveren. VSM richt zich op twee dingen: hoe snel de door de klant gevraagde functies of updates worden geleverd en of de klant de waarde van die wijzigingen realiseert. Volgens Forrester heeft "Het beheer van waardestromen (VSM) het potentieel om het proces van het financieren, bouwen, beheren en onderhouden van software volledig op grote schaal te transformeren." De wortels van het beheer van waardestromen liggen in lean manufacturing en sluiten aan op het Toyota Production System (TPS) uit de jaren vijftig. Deze systematische aanpak is bedoeld om een sneller rendement mogelijk te maken en producten van hogere kwaliteit te leveren. Het beheer van waardestromen helpt de C-suite in contact te brengen met Agile- en DevOps-teams om op elkaar af te stemmen voor klanttevredenheid. Het beheren van waardestromen biedt:
Snellere levering van klantgerichte producten, waardoor het concurrentievermogen wordt verhoogd en de inkomsten toenemen
Betere klantervaringen, wat leidt tot positieve beoordelingen en doorverwijzingen
Betere betrokkenheid van werknemers bij cross-functionele teams, waardoor mensen het grote geheel kunnen zien in plaats van alleen hun silo
Besluitvorming op basis van gegevens en inzichten voor toekomstige investeringen
Wat is een waardestroom?
Gartner definieert een waardestroom als 'de reeks activiteiten die nodig zijn om een product, service of ervaring te leveren aan een klant: intern of extern.' Waardestromen bestaan al in bedrijven, zelfs als ze niet als zodanig zijn gelabeld. Als je je waardestromen begrijpt, kun je betere investeringsbeslissingen nemen, zodat er geen middelen worden verspild. Waardestromen omvatten elk contactpunt op het traject, van het genereren van ideeën tot het leveren van waarde aan klanten. Zonder deze kennis weet je niet wat werkt en waar je problemen hebt. Je kunt bijvoorbeeld te maken krijgen met langdurige vertragingen tijdens overdrachten tussen teams, wat de productiviteit en kwaliteit negatief beïnvloedt.
Waardestromen in softwareontwikkeling
Waardestromen en DevOps zijn beide gebaseerd in de principes van lean. Denken en werken als waardestromen helpen technologieteams bij het identificeren en prioriteren van verbeterpunten op het gebied van softwareontwikkeling. DevOps biedt praktijken en tools om de levering van waardestromen te verbeteren. Door te focussen op stroomoptimalisatie, worden inefficiënties geïdentificeerd en worden processen gestroomlijnd.
Wat is waardestroommapping?
Waardestroommapping is een visuele samenwerkingstechniek die wordt gebruikt om waardestromen te beschrijven door de stroom van activiteiten te identificeren en te analyseren die nodig is om een product of service aan een klant te leveren. Waardestroommapping brengt afhankelijkheden, blokkades, inefficiënties en verspilling aan het licht, waardoor budgetten worden overschreden en de levering wordt vertraagd. Om waardestromen in kaart te brengen, verzamelen cross-functionele teams gegevens om de stappen te identificeren en de actieve tijd en inactieve tijd voor elke stap te meten. Hierdoor kunnen teams de cyclustijd berekenen voor de waardestroom door alle actieve en inactieve tijden bij elkaar op te tellen. Door whiteboards of mappingsoftware te gebruiken om visueel samen te werken, kunnen teams items aanwijzen als items die waarde toevoegen of geen waarde toevoegen vanuit het perspectief van de klant. Ze kunnen ook probleemgebieden bepalen, zoals een team met te weinig personeel dat andere teams vertraagt om verder te werken.
Waarom is het beheer van waardestromen belangrijk?
Er is vaak een verschil tussen wat klanten zeggen dat ze willen (verkregen uit bronnen zoals klantenservice of salesteams) en wat er daadwerkelijk wordt geleverd. Het gebrek aan effectieve communicatie tussen bedrijfsteams en technologieteams is een onderdeel van het probleem. Hoewel de C-suite zich richt op doelen en algemene strategieën, spreken technologieleiders vaak in termen van leveringsfrequentie en technische outputs. Leiders en hun teams moeten een gemeenschappelijke taal en betere communicatiekanalen ontwikkelen om de doelstellingen en ervaringen van klanten op elkaar af te stemmen. Het beheer van waardestromen vergemakkelijkt communicatie tussen teams om de informatiestroom en waardecreatie te verbeteren. De klant vraagt een functie aan via sales- of supportteams, productteams ontwerpen de functionaliteit, technische teams bouwen de software en het product wordt geleverd. Met een vertegenwoordiger van elk team in een cross-functioneel team kan het juiste product efficiënter en effectiever worden geleverd. De problemen die door VSM worden aangepakt, zijn onder andere:
Frustratie van klanten over het huidige aanbod
Trage levering van bugfixes en nieuwe functies of producten
Marktaandeel verliezen aan concurrenten die zich snel aanpassen aan marktveranderingen
Minder middelen als gevolg van ontslagen werknemers en andere kostenbesparende maatregelen
Agile en/of digitale transformaties leveren niet zo effectief als gewenst
Gebrek aan zichtbaarheid in de hele organisatie als gevolg van silo's en uiteenlopende gegevens
Organisatiestructuur die niet is ontworpen voor waardecreatie

Wat zijn de voordelen van het beheer van waardestromen?
Zodra waardestromen zijn geïdentificeerd en toegewezen, kunnen bedrijven deze analyseren om nieuwe producten of functies aan te maken. Ze kunnen realtime, datagestuurde inzichten in de waardestroom gebruiken om betere zakelijke beslissingen te nemen, zoals wat klanten van huidige producten vinden en wat er moet veranderen. In plaats van te investeren in individuele projecten, kan de volledige waardestroom worden gefinancierd, wat flexibiliteit biedt om zich aan te passen aan veranderende behoeften van klanten zonder dat er nieuwe budgetaanvragen nodig zijn. De voordelen van het beheer van waardestromen zijn onder andere:
Toegenomen voorspelbaarheid.
Inzicht in de volledige waardestroom helpt om onzekerheid en verrassingen te verminderen die tot gemiste deadlines leiden.
Hogere klanttevredenheid.
Snel reageren op aanvragen van klanten kan hun ervaring en de reputatie van het bedrijf verbeteren.
Verbeterde productiviteit.
Door activiteiten te stroomlijnen en blokkades te verminderen, kunnen teams sneller ideeën bedenken, testen en leveren.
Lagere kosten.
Het identificeren van onnodig werk en verspilde middelen bespaart geld en tijd.
Betere software.
Door handmatige taken te automatiseren, komt er tijd vrij voor innovatie en wordt de kans op fouten en defecten verkleind.
Verbeterde zichtbaarheid van begin tot eind.
Omdat er in de hele organisatie realtime gegevens beschikbaar zijn, kunnen mensen initiatieven volgen en zich aanpassen aan veranderende bedrijfsprioriteiten.
Meer innovatie en beter moreel.
Ontwikkelaars vinden het fijner als ze zich kunnen richten op producten die echt belangrijk zijn voor klanten.
Oplossingen voor het beheer van waardestromen
Oplossingen voor het beheer van waardestromen helpen leiders om waardestroomdenken in de hele organisatie naar een hoger niveau te tillen om de effectiviteit van hun teams te vergroten. Teams hebben realtime toegang nodig tot gegevens en rapporten om te begrijpen of processen soepel verlopen. Ze kunnen de tools van VSM gebruiken om continue verbetering te stimuleren en investeringen te correleren aan de waarde van de klant. Softwareoplossingen van VSM vergroten de samenwerking zonder teams te vertragen door:
Het bieden van een geïntegreerde visie die bedrijfssilo's doorbreekt
Mensen, werk en tijd op elk niveau van het bedrijf te koppelen
Gegevens te combineren uit verschillende bronnen, zoals heterogene toolchains
Een enkele bron van waarheid aanmaken zonder de dagelijkse gang van zaken te verstoren
Voortdurende versterking van de best practices op het gebied van Agile
We werken met jouw gewenste framework, zoals SAFe, Scrum @Scale, LeSS, Disciplined Agile, Spotify of hybrides.
We bieden tools voor teams op elk niveau, van leidinggevenden tot releaseketens
Proactief omgaan met afhankelijkheden tussen teams om de voorspelbaarheid te verbeteren
Een omgeving aanmaken waarin voortdurend wordt verbeterd met kortere feedbackloops
Meten en analyseren van de dingen die er toe doen
Met oplossingen van VSM kunnen teams autonoom handelen om door klanten gevraagde producten te leveren, vervolgens te analyseren of deze hebben geleid tot tastbare, meetbare veranderingen in de klantervaringen, en te reageren op wat ze leren.
Statistieken van waardestromen voor het meten van doelen en voortgang
Veel bedrijven hebben te kampen met een gebrek aan zichtbaarheid en uitgebreide rapporten, vooral bedrijven die sterk op elkaar zijn afgestemd. Oplossingen voor waardestroombeheer doorkruisen silo's en brengen uiteenlopende gegevens samen om je de statistieken te geven die je nodig hebt en bruikbare inzichten.
Stroomstatistieken
Stroomstatistieken evalueren de mate van waardelevering in relatie tot de gewenste bedrijfsresultaten.
Stroomsnelheid
meet het aantal waarde-eenheden dat gedurende een bepaalde periode binnen een waardestroom is voltooid.
Stroomtijd
meet de tijd vanaf het moment dat wordt begonnen met werk aan een eenheid van waarde binnen een waardestroom tot het moment dat deze aan een klant wordt vrijgegeven. Te lange doorlooptijden kunnen wijzen op inefficiënties of knelpunten.
Stroombelasting
meet het werk in uitvoering (WIP), een belangrijke indicator die verband houdt met inefficiënties binnen een waardestroom.
Stroomefficiëntie
meet het aandeel van de tijd waaraan waardeeenheden actief worden gewerkt in vergelijking met de totale stroomtijd. Een lage stroomefficiëntie kan duiden op lange wachttijden tussen de stappen, wat leidt tot grote wachtrijen en meer WIP.
Stroomverdeling
meet de verhouding tussen de bovenstaande stroomitems die in een bepaalde periode zijn voltooid. Het is nuttig om prioriteit te geven aan het werk dat nodig is om bedrijfs- en teamdoelen te bereiken.
DORA-statistieken
DORA-statistieken evalueren en verbeteren de effectiviteit van DevOps-teams.
Doorlooptijd voor wijzigingen
betreft de tijdsduur tussen het moment dat een codewijziging wordt vastgelegd in de trunkbranch en wanneer deze geïmplementeerd kan worden.
Foutpercentage van wijzigingen
is het percentage codewijzigingen waarvoor hot fixes of andere hersteloplossingen na productie nodig zijn.
Implementatiefrequentie
meet hoe vaak nieuwe code wordt geïmplementeerd in de productie en kan worden gebruikt om de snelheid en flexibiliteit van een team te meten.
Gemiddelde tijd tot herstel (MTTR, Mean Time to Recovery)
meet hoelang de oplossing van een gedeeltelijke serviceonderbreking of totale storing duurt.
Doelstellingen en belangrijke resultaten (Objectives en Key Results of OKR's)
Ondernemingen moeten ervoor zorgen dat teams hun werk doen in lijn met de doelstellingen van het bedrijf. Doelstellingen en belangrijkste resultaten (OKR's) bestaan uit twee componenten: het doel dat je wilt bereiken en de belangrijkste resultaten die je succes meten. De C-suite stelt OKR's op hoog niveau vast die verband houden met de missie, visie en kernwaarden van de organisatie. Individuele teams beslissen hoe ze die doelen bereiken door hun eigen OKR's op teamniveau te stellen. OKR's kunnen op kwartaalbasis worden ingesteld, zodat beslissingen sneller kunnen worden aangepast of doorgezet op basis van nieuwe gegevens of marktveranderingen. OKR's worden bijgehouden zodat je de huidige status van activiteiten kunt zien, zoals of ze op tijd zijn, risico lopen of geblokkeerd zijn.
Hoe verbetert VSM de waardecreatie?
Waardecreatie is erop gericht om ervoor te zorgen dat er aan de juiste items wordt gewerkt, dat de items leveren wat de bedoeling is en dat ze bijdragen aan de volgende cyclus van productontwikkeling. Hoewel er meestal prioriteit wordt gegeven aan de ontwikkeling van nieuwe producten of functies in plaats van systemische verbeteringen, is een holistische kijk vereist bij investeringen in functies, defecten, technische schulden en risico's.Waardecreatie kan worden opgedeeld in twee categorieën:
Outputs (gezondheid van waardestromen)
Outputs zijn gekoppeld aan de werkstroom van idee tot realisatie en levering van een continue stroom van waarde voor klanten. Door verbeteringen aan te brengen in het onderliggende leveringssysteem (mensen, processen en technologie) komt er meer tijd vrij voor waardecreatie. Door de werkverdeling en cyclustijden te meten, kunnen teams zien welke invloed hun acties hebben op hun vermogen om nieuwe functies aan te bieden en de capaciteit te verhogen.
Resultaten (klantervaringen)
Door de klantervaring te meten, kunnen teams zien of ze de gewenste klantwaarde hebben geleverd, zoals een verhoogd aantal klanten of positieve beoordelingen. Deze statistieken (gebaseerd op gegevens, feedback en analyses) geven teams de informatie die nodig is om toekomstige beslissingen te nemen en investeringen te maken.
Sjablonen
Jira-sjablonen, klaar voor gebruik
Bekijk onze bibliotheek met op maat gemaakte Jira-sjablonen voor verschillende teams, afdelingen en workflows.
Producthandleiding
Een uitgebreide introductie tot Jira
Maximaliseer je productiviteit met de essentiële functies en de beste werkwijzen uit deze stapsgewijze handleiding.
Git-handleiding
De Git-basics onder de knie krijgen
Gebruik de tutorials en tips in deze Git-handleiding om de basis te leren. Handig voor iedereen: van beginners tot experts.