- What is Agile?
- Agile Manifesto
- Overview
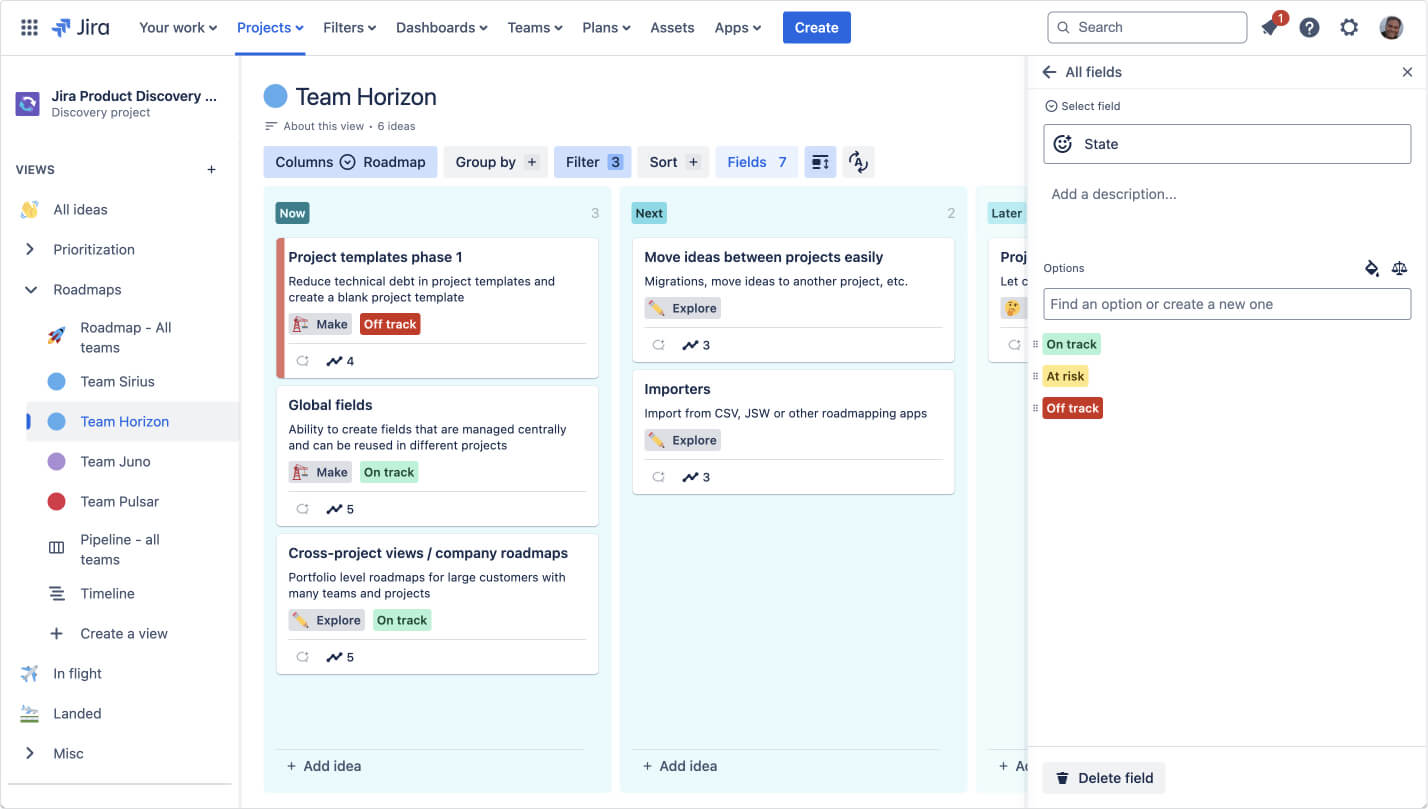
- Product Roadmaps
- Product Manager
- Tips for new product managers
- Roadmaps
- Tips for presenting product roadmaps
- Requirements
- Product analytics
- Product development
- Remote product management
- Minimal viable product
- Product discovery
- Product specification
- Product development strategy
- Product development software
- New product development process
- Product management KPIs
- Net Promoter Score (NPS)
- Product critique
- Prioritization frameworks
- Product features
- Product management tools
- Product Lifecycle Management
- 9 best roadmap software for teams
- Product launch checklist
- Product strategy
- Product engineering
- Product operations
- Portfolio management
- AI and product management
- Growth product management
- Product metrics
- Product release
- Feature request
- Product launch
- Product planning
- Product launch event
- Product operating model
- Product design
- Value Stream Management
- DevOps
- All articles
- What is Agile?
- Agile Manifesto
- Overview
- Product Roadmaps
- Product Manager
- Tips for new product managers
- Roadmaps
- Tips for presenting product roadmaps
- Requirements
- Product analytics
- Product development
- Remote product management
- Minimal viable product
- Product discovery
- Product specification
- Product development strategy
- Product development software
- New product development process
- Product management KPIs
- Net Promoter Score (NPS)
- Product critique
- Prioritization frameworks
- Product features
- Product management tools
- Product Lifecycle Management
- 9 best roadmap software for teams
- Product launch checklist
- Product strategy
- Product engineering
- Product operations
- Portfolio management
- AI and product management
- Growth product management
- Product metrics
- Product release
- Feature request
- Product launch
- Product planning
- Product launch event
- Product operating model
- Product design
- Value Stream Management
- DevOps
- All articles
What is a product operating model & how to create one from scratch
The product operating model aligns teams, drives customer value, and improves agility to deliver successful products consistently. Learn more.
Get the free product discovery template
Align your team from idea to delivery. Prioritize ideas, create custom roadmaps, and ensure full visibility across all stages.
For any organization, the ability to deliver value quickly and consistently is crucial. Without a structured framework to align teams, prioritize work, and adapt to changing demands, staying ahead of the competition becomes increasingly difficult.
This is where the product operating model comes in. By establishing a clear product vision, building cross-functional teams, and implementing a clear agile product strategy, companies can improve collaboration, streamline workflows, and achieve faster, more reliable results.
In this article, we’ll explore the core components of the product operating model and how it can drive better outcomes for your business.
Key takeaways
A product operating model is a framework that aligns teams, processes, and technology to deliver customer-centric products quickly and efficiently.
It helps align teams around customer value, ensuring all departments work together to solve real-world problems and achieve business outcomes.
The model improves agility by empowering small, cross-functional teams to make fast decisions and iterate on solutions quickly.
Continuous learning and iteration are at the heart of the model, ensuring products evolve based on user feedback and market insights to maintain long-term success.
What is a product operating model?
What is a product operating model?
A product operating model is a blueprint that defines how an organization structures its teams, processes, and technology to deliver products that consistently satisfy customer needs.
It treats products as if they are never truly finished. This outlook centers on a product's entire lifecycle, allowing it to evolve through ongoing iteration and improvement.
The model's primary function is to create a solid connection between business strategy, people, and processes. Instead of simply building a list of product features, teams are tasked with solving specific customer problems and getting clear results.
The goal is to always look for tangible results for both the customer and the business.
Benefits of using a product operating model
Aligns product teams around customer value
The product operating model ensures that all teams—from product management and design to engineering and marketing—share a common goal: solving real-world customer problems.
This collective focus helps break down departmental silos and replace fragmented efforts with unified, purposeful work. Success is no longer measured by individual team metrics but by the collective impact on the end user and business outcomes.
Improves agility for faster decision-making and development
A product operating model significantly reduces bureaucracy and delays by giving small teams the autonomy to make decisions.
For example, teams can rapidly test hypotheses, gather user feedback, and foster incremental continuous improvement without waiting for approval from multiple layers of management. This flexibility allows organizations to respond quickly to market changes, competitive threats, and emerging customer needs.
Improves collaboration and communication among cross-functional teams
The model is built on the foundation of cross-functional teams where diverse skill sets are brought together to own a product or a specific part. Instead of passing the buck to the next department, teams work side-by-side, sharing insights and expertise.
This improves the quality of solutions and builds stronger, more cohesive teams by fostering a culture of shared responsibility and open communication.
Focuses on outcomes over outputs to deliver far-reaching results
A critical shift in this model is moving the focus from outputs (e.g., shipping a certain number of features or hitting a release date) to broader outcomes (e.g., increasing customer retention or improving user satisfaction). This distinction encourages teams to think about the "why" behind their work and measure success based on the positive impact on the customer and the business..
Supports long-term product vision with continuous evolution
Unlike projects that have a defined end date, a product operating model emphasizes the longevity and continuous evolution of a product. It encourages teams to maintain a product roadmap that is continuously informed by user data and market insights.
This commitment to ongoing investment ensures that the product remains relevant and valuable over time, allowing the organization to build a sustainable competitive advantage.
Six key components of a product operating model
A successful product operating model is a comprehensive system built on several interconnected building blocks. These six components work in harmony to align the entire organization around a common purpose and efficient product delivery.
1. Product vision and strategy
The product vision articulates the role of the product long into the future, while the product strategy outlines the critical problems to be solved to achieve that vision. This clarity guides decision-making and ensures that all efforts move the business toward its strategic objectives.
2. Customer-centric decision-making
The model places customer needs at the very heart of the product development process. Teams embed user insights into every choice around the product’s creation, from initial ideation to final delivery.
You need regular feedback from user interviews, data analysis, and app feedback to confirm ideas and make sure the solution solves customer problems.
3. Cross-functional teams
These are small, durable teams composed of members from different disciplines, such as product management, design, and engineering. Rather than working in isolated departments, these teams share control of product development or specific problems end-to-end.
Following this structure streamlines communication, reduces handoffs, and fosters a deep sense of accountability.
4. Agile processes
Adopting agile methodologies, such as Scrum or Kanban, is critical for enabling flexible, iterative delivery. These frameworks provide a structured way for teams to manage their work.
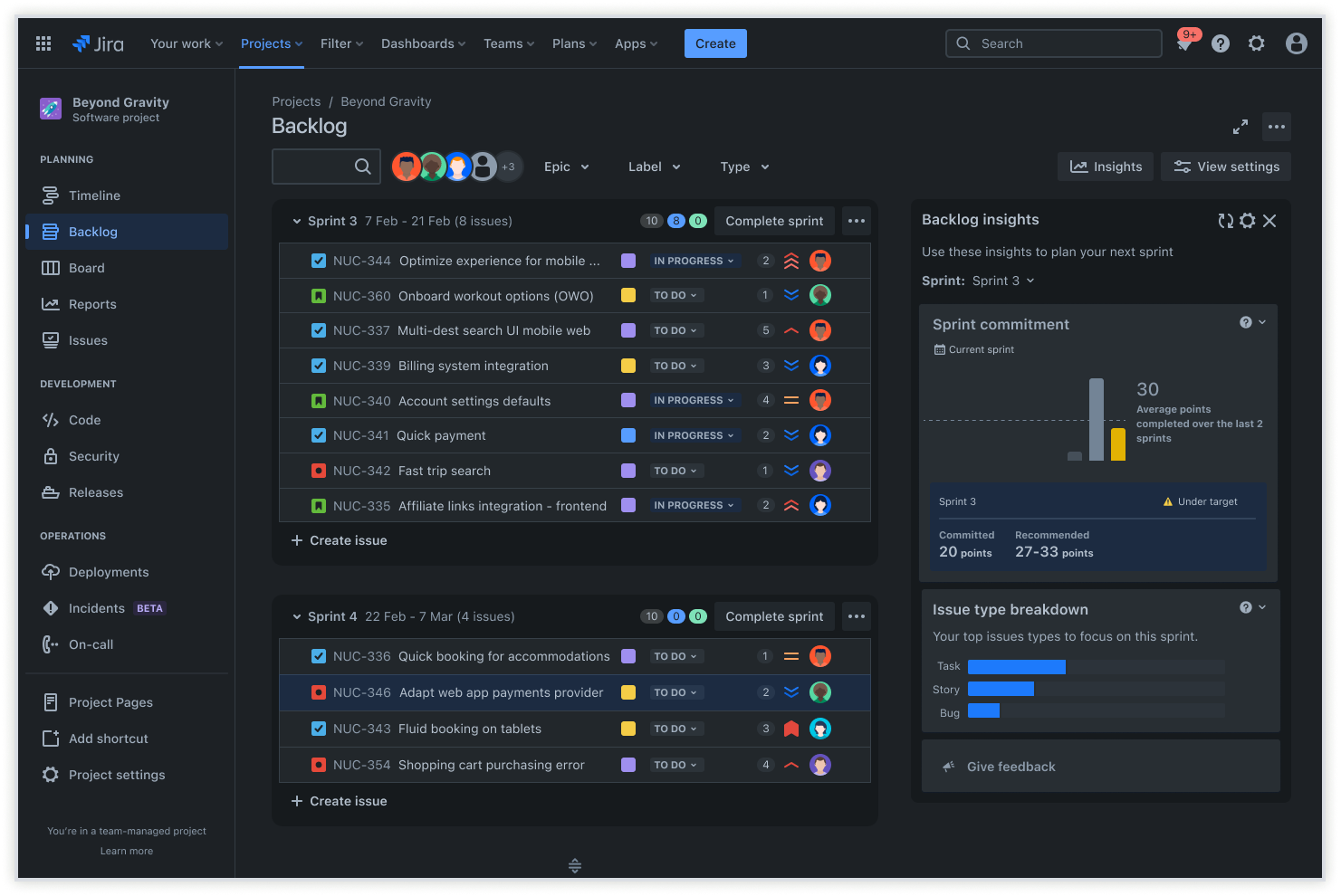
It provides your team with regular opportunities to take stock, like sprint planning, daily standups, and retrospectives. These practices promote transparency, adaptability, and continuous improvement, allowing teams to deliver value in small, frequent releases.
5. Continuous learning and improvement
The model creates a "build, measure, learn" loop, where teams create a prototype, test it with users, analyze the results, and use those insights to refine the product. With this iterative cycle, you minimize waste by making sure resources are only invested in solutions that have been validated and proven to be valuable.
6. Product-focused technology infrastructure
Key product management tools and platforms enable this model to function at scale. For example, integrated systems can be dedicated to idea management, product metrics, project tracking, and collaboration (such as Jira, Confluence, and Figma).
A comprehensive tech stack supports cross-functional teams, streamlines workflows, and provides the data needed for informed, strategic decisions.
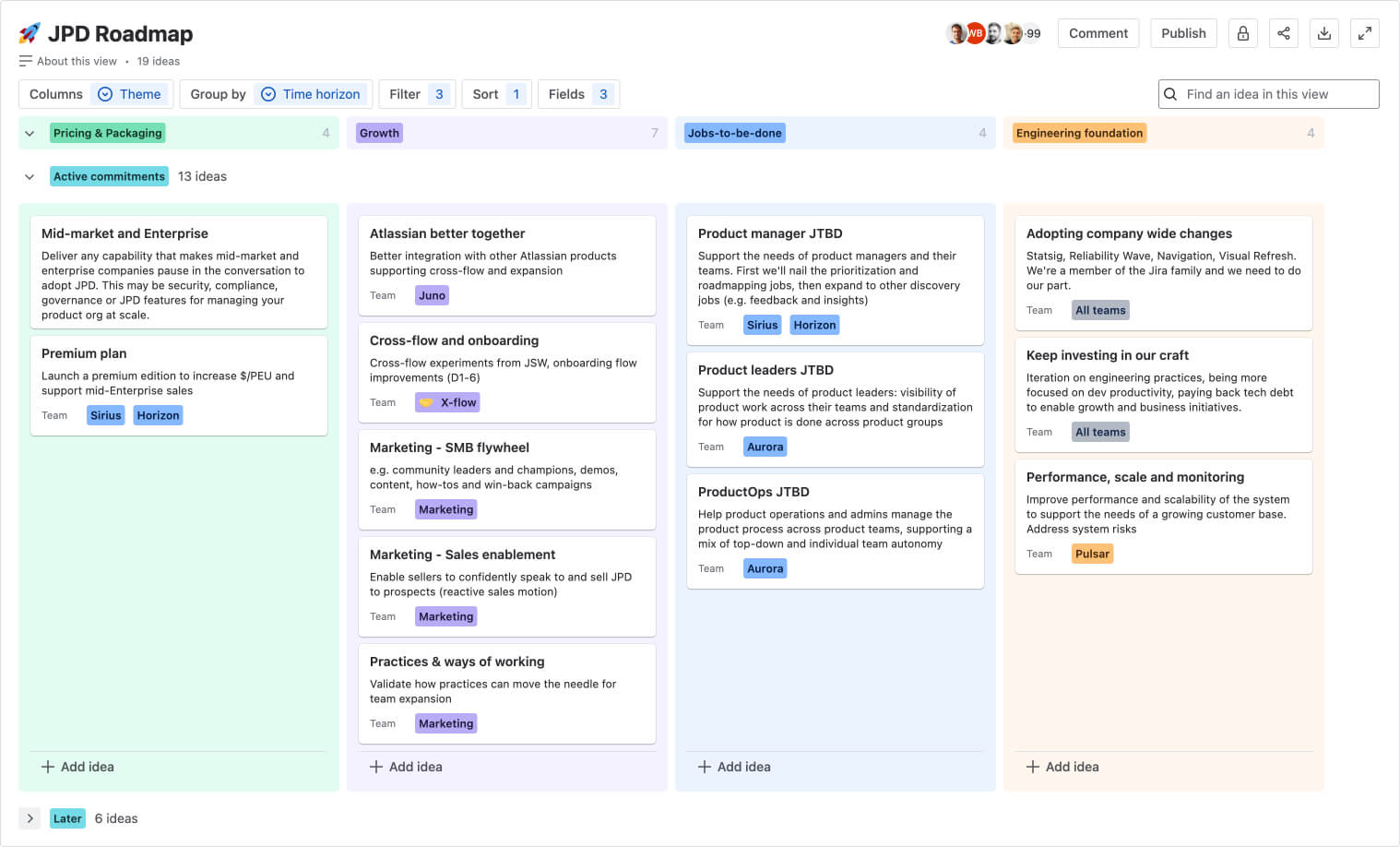
Product operating model examples
To illustrate how a product operating model works in practice, here are three hypothetical scenarios that demonstrate the benefits mentioned above.
B2B software company example: Aligning around customer value
A company that builds enterprise communication software traditionally organizes its teams by function, with separate departments for engineering, sales, and support. When a competitor launches a new feature addressing a long-standing customer pain point, the company realizes it must adapt.
To better align with customer needs, the company transitions to a product operating model, reorganizing its teams around customer segments like "small businesses" and "large enterprises." Each team takes full ownership of its segment's needs.
The small business team, with direct access to customer support data and feedback, identifies that a confusing onboarding flow is driving up churn rates.
They work collaboratively to redesign the onboarding process, aiming for a significant reduction in churn within one quarter.
E-commerce platform example: Improving speed and agility
A fast-growing e-commerce platform is frustrated with its slow development cycles. Each new feature requires approval from multiple departments, leading to delays and weeks of waiting.
By shifting to a product operating model, the company creates autonomous teams focused on specific areas of the platform, such as the "checkout experience" or "search functionality." The "checkout experience" team is given a clear objective: reduce cart abandonment.
Using real-time data and user session recordings, the team quickly identifies a bug and a confusing payment form.
Without needing approval from other departments, the team deploys a fix and simplifies the payment form within a two-week sprint, resulting in a noticeable increase in completed transactions.
Financial services app example: Focusing on outcomes over outputs
A mobile banking app’s development team is pressured to meet a high volume of new features each quarter. While deadlines are met, user engagement fails to increase.
The company transitions to a product operating model, reframing the team’s focus around specific customer outcomes—like increasing the number of users setting up savings goals.
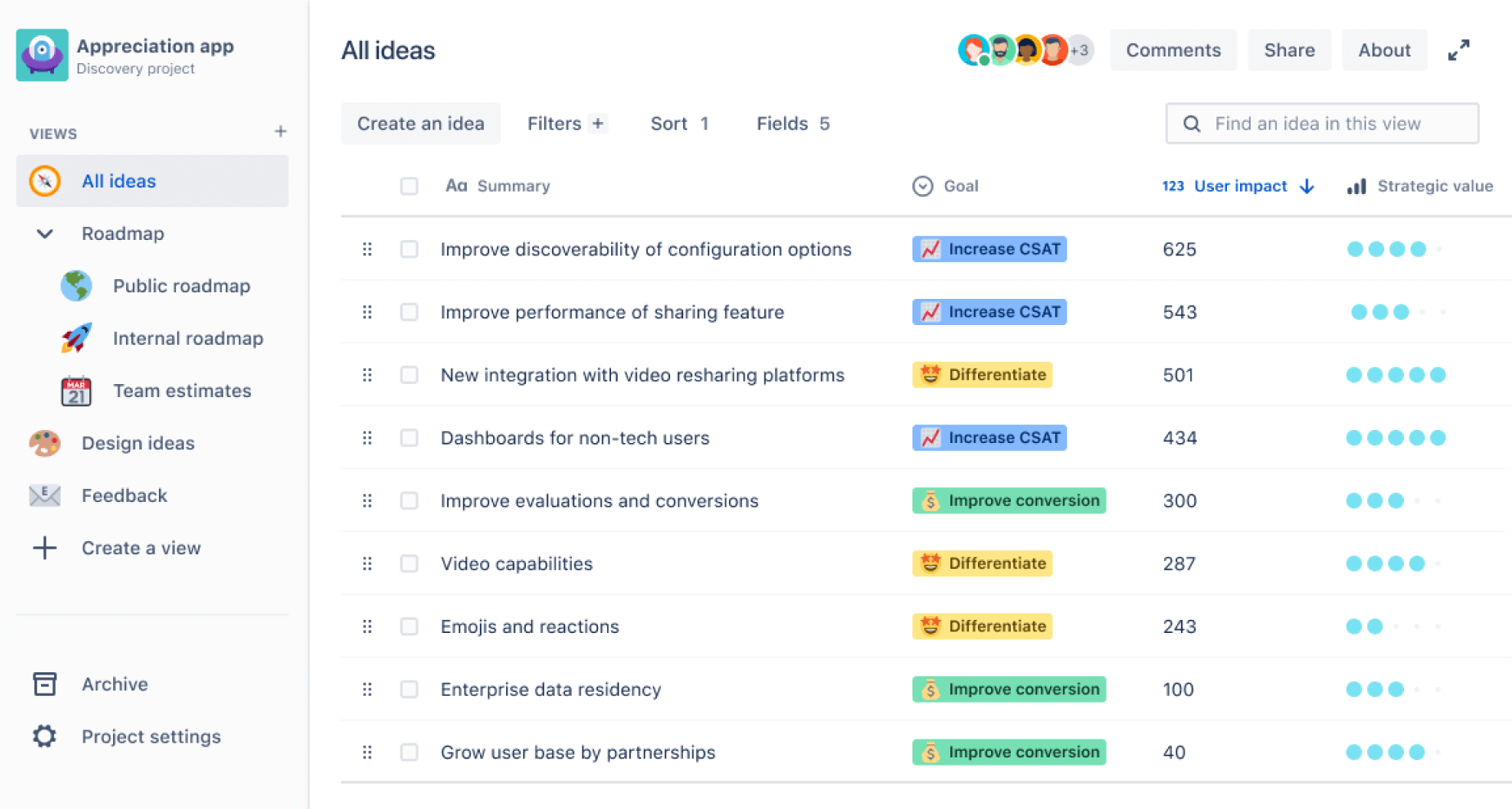
The team uses Jira Product Discovery to capture, organize, and prioritize customer insights that would otherwise be lost across various systems.
Rather than simply adding a "set a savings goal" feature, the team decides to gamify the savings process, introducing progress bars and celebratory animations to make it engaging.
This shift in approach helps the team focus on outcomes, making saving money feel rewarding and easy, which could increase the number of users who successfully achieve their savings goals.
How to create and apply a product operating model in 6 steps
By implementing a product operating model in a structured way, you ensure a smooth transition and maximize the benefits for your organization. Here is a step-by-step approach to get started:
Step 1: Assess the current state of product development and delivery
Begin by evaluating your existing workflows, team structures, and decision-making processes. Identify what's working well, what's causing bottlenecks, and where you have gaps in collaboration or customer understanding. This assessment provides a baseline and helps you pinpoint the most critical areas for improvement.
Step 2: Define product vision and strategy to align teams
Work with key stakeholders—including executives, product leaders, and senior technical staff—to define a compelling product vision. This vision should be customer-focused and ambitious. From this, create a clear product strategy that outlines the most important problems to solve and the outcomes you want to achieve.
Step 3: Map out core processes to streamline product delivery
Document your core product development and delivery processes. This includes everything from idea intake and prioritization to the agile ceremonies teams will follow. The goal is to create clarity on how work flows, who is responsible for what, and how teams should collaborate.
Step 4: Establish governance to guide accountability
While autonomy of teams leads to agility, it does come with potential for chaos. A clear governance framework avoids this by defining decision rights and clarifying the roles and responsibilities of each team and individual.
Establish prioritization frameworks to ensure that the most valuable work is always addressed first. This structure provides the necessary guardrails for teams to operate independently while remaining aligned with strategic goals.
Step 5: Use the right tools to support product teams
Select technology platforms that are designed to support agile product management and collaborative workflows. These tools should be integrated so updates are in one area to ensure a seamless flow of information from customer feedback to the engineering backlog.
Platforms like Jira and Confluence provide a single source of truth for all product-related work, keeping strategy, execution, and team collaboration aligned.
Step 6: Iterate and refine based on feedback
Begin with a pilot program, applying the new model to a small number of teams or a specific product line. Gather feedback from the teams to understand what's working and what's not.
Use this feedback to modify the operating model itself, adjusting practices, roles, and tools as you scale.
Use Jira Product Discovery for customer-centric success
A product operating model is a powerful framework, but it requires the right tools to bring it to life. Jira Product Discovery supports the model by providing a central hub for all product-related work, from initial idea to final outcome.
It guides teams in acting on customer insights, making data-driven decisions, and maintaining a shared sense of purpose.
With Jira Product Discovery, every product decision is rooted in customer-centric thinking because ideas can be linked directly to their source—be it customer feedback, stakeholder requests, or market analysis.
It also helps teams prioritize ideas based on business impact, customer value, and strategic alignment, rather than just stakeholder demand. Teams can use flexible prioritization frameworks to score and rank ideas, making it clear which opportunities will deliver the most meaningful results.
Finally, the platform's intuitive interface allows product managers, designers, engineers, and stakeholders to collaborate on ideas, provide feedback, and understand the "why" behind what's being built. This shared, cross-functional context ensures everyone has visibility into the product roadmap.
Try Jira Product Discovery free
Recommended for you
Templates
Ready-made Jira templates
Browse our library of custom Jira templates for various teams, departments, and workflows.
Product guide
A comprehensive introduction to Jira
Use this step-by-step guide to discover essential features and the best practices to maximize your productivity.
Git Guide
Understanding the Basics of Git
From beginners to advanced experts, use this guide to Git to learn the basics with helpful tutorials and tips.