- What is Agile?
- Agile Manifesto
- Overview
- Product Roadmaps
- Product Manager
- Tips for new product managers
- Roadmaps
- Tips for presenting product roadmaps
- Requirements
- Product analytics
- Product development
- Remote product management
- Minimal viable product
- Product discovery
- Product specification
- Product development strategy
- Product development software
- New product development process
- Product management KPIs
- Net Promoter Score (NPS)
- Product critique
- Prioritization frameworks
- Product features
- Product management tools
- Product Lifecycle Management
- 9 best roadmap software for teams
- Product launch checklist
- Product strategy
- Product engineering
- Product operations
- Portfolio management
- AI and product management
- Growth product management
- Product metrics
- Product release
- Feature request
- Product launch
- Product planning
- Product launch event
- Product operating model
- Product design
- Value Stream Management
- DevOps
- All articles
- What is Agile?
- Agile Manifesto
- Overview
- Product Roadmaps
- Product Manager
- Tips for new product managers
- Roadmaps
- Tips for presenting product roadmaps
- Requirements
- Product analytics
- Product development
- Remote product management
- Minimal viable product
- Product discovery
- Product specification
- Product development strategy
- Product development software
- New product development process
- Product management KPIs
- Net Promoter Score (NPS)
- Product critique
- Prioritization frameworks
- Product features
- Product management tools
- Product Lifecycle Management
- 9 best roadmap software for teams
- Product launch checklist
- Product strategy
- Product engineering
- Product operations
- Portfolio management
- AI and product management
- Growth product management
- Product metrics
- Product release
- Feature request
- Product launch
- Product planning
- Product launch event
- Product operating model
- Product design
- Value Stream Management
- DevOps
- All articles
What is product design? How to get started and essential tools to succeed
Product design is the process of creating functional and user-friendly products. Learn the key principles and steps involved.
Get the free product discovery template
Align your team from idea to delivery. Prioritize ideas, create custom roadmaps, and ensure full visibility across all stages.
Product design shapes every interaction we have with the world around us, from the smartphone or desktop you're reading this on to the bed you sleep in at night. It's the thoughtful process of creating solutions that not only look good, but also solve real problems for real people.
This product management guide walks you through what product design means, its core principles, and the necessary steps to take to turn ideas into successful products.
What is product design?
What is product design?
Product design is the strategic process of identifying user problems and creating solutions that are both functional and beneficial to use. It combines creative thinking with business objectives, ensuring that every design decision serves both user needs and company goals.
A successful product manager isn't just concerned with making products look good. They research, test, and refine ideas to create products that people genuinely find valuable.
At its heart, product design bridges the gap between what users want and what's technically and financially feasible. It requires understanding human behavior, market dynamics, and technological constraints while maintaining a clear vision of the end goal.
The best product design feels invisible to users because everything just works the way they expect it to.
Why is product design important?
Why is product design important?
Good product design directly impacts business success by creating emotional connections between users and brands. When products are intuitive and easy to use, customers become loyal advocates who recommend them to others, driving organic growth and reducing acquisition costs.

On the other hand, poor design can doom innovative ideas. Even with cutting-edge technology and product features, products can fail without a solid user experience and product design.
What is a product designer?
What is a product designer?
A product designer wears many hats and is responsible for overseeing the full lifecycle of a product, from research and ideation to prototyping, testing, and launch. This role must balance user needs, technical feasibility, and business goals to create solutions that are both functional and valuable.
To become a product designer, it’s helpful to obtain a certification in UX/UI design and have the proper experience working in a related industry. In the U.S., product designers typically earn between $90,000–$120,000 annually, depending on title and level of expertise.
Product design vs. UX design
Product design vs. UX design
While product design and UX design overlap, they serve different roles. UX design focuses specifically on how users interact with and experience a product, concentrating on usability, information architecture, and user flows.
Product design takes a broader view, encompassing not just the user experience but also business strategy, technical constraints, market positioning, and product management considerations.
While a UX designer might perfect how users navigate a checkout process, a product designer would also consider whether that checkout process aligns with the company's business model and brand identity.
The 5 core principles of product design
These fundamental principles guide effective product design and help create solutions that truly serve users while achieving business objectives:
1. User-centered design
1. User-centered design
Putting your target customers at the center of every design decision means deeply understanding their needs, frustrations, and goals before creating solutions. This approach requires regular user research, testing prototypes with real people, and iterating based on feedback rather than assumptions.
Example: Spotify uses features like Discover Weekly, which uses listening data to create personalized playlists that genuinely surprise and benefit users.
2. Functionality and usability
2. Functionality and usability
Products must work reliably and be easy to use, or even the most beautiful design will fail. Regular usability testing reveals where people struggle with a product, helping companies identify areas for improvement.
Example: Airbnb constantly tests different versions of their booking flow to reduce friction and increase conversion rates.
3. Aesthetics and brand alignment
3. Aesthetics and brand alignment
Visual design influences how people perceive and trust a product before they even try it. Clean, professional aesthetics signal quality and reliability, while playful designs can convey innovation and approachability.
Example: Apple consistently uses clean lines, premium materials, and includes subtle details across all products to create a recognizable brand experience that commands premium pricing.
4. Sustainability
4. Sustainability
Environmental consciousness has become increasingly crucial in modern product design, as consumers prefer brands that align with their values.
Example: Patagonia built its entire brand around sustainable practices, using recycled materials and encouraging customers to repair rather than replace products.
5. Innovation
5. Innovation
Creative problem-solving and fresh perspectives help products stand out in crowded markets while addressing user needs in new ways.
Example: Netflix innovated by recognizing that people wanted entertainment on demand rather than following traditional TV schedules, leading to the streaming model that transformed how we consume television shows and movies.
Every essential step of the product design process
Successful product design follows a structured process that moves from initial research through final launch. These five core phases provide a framework for turning ideas into market-ready solutions:
Step 1. Conduct market research and gather user insights
Step 1. Conduct market research and gather user insights
Research is the foundation of every successful product, as it shows businesses what users actually need versus what we think they need. This phase involves analyzing market trends, studying competitors, and engaging directly with potential users through surveys, interviews, and observational studies.

Tools like user personas, journey maps, and competitive analysis help teams synthesize findings into actionable insights.
Step 2. Brainstorm, validate, and prioritize concepts
Step 2. Brainstorm, validate, and prioritize concepts
Teams generate multiple potential solutions through structured brainstorming sessions using techniques like design sprints, mind mapping, and rapid sketching.
After generating concepts, teams validate them against user needs and business constraints to identify the most promising directions through quick user interviews or technical feasibility assessments.
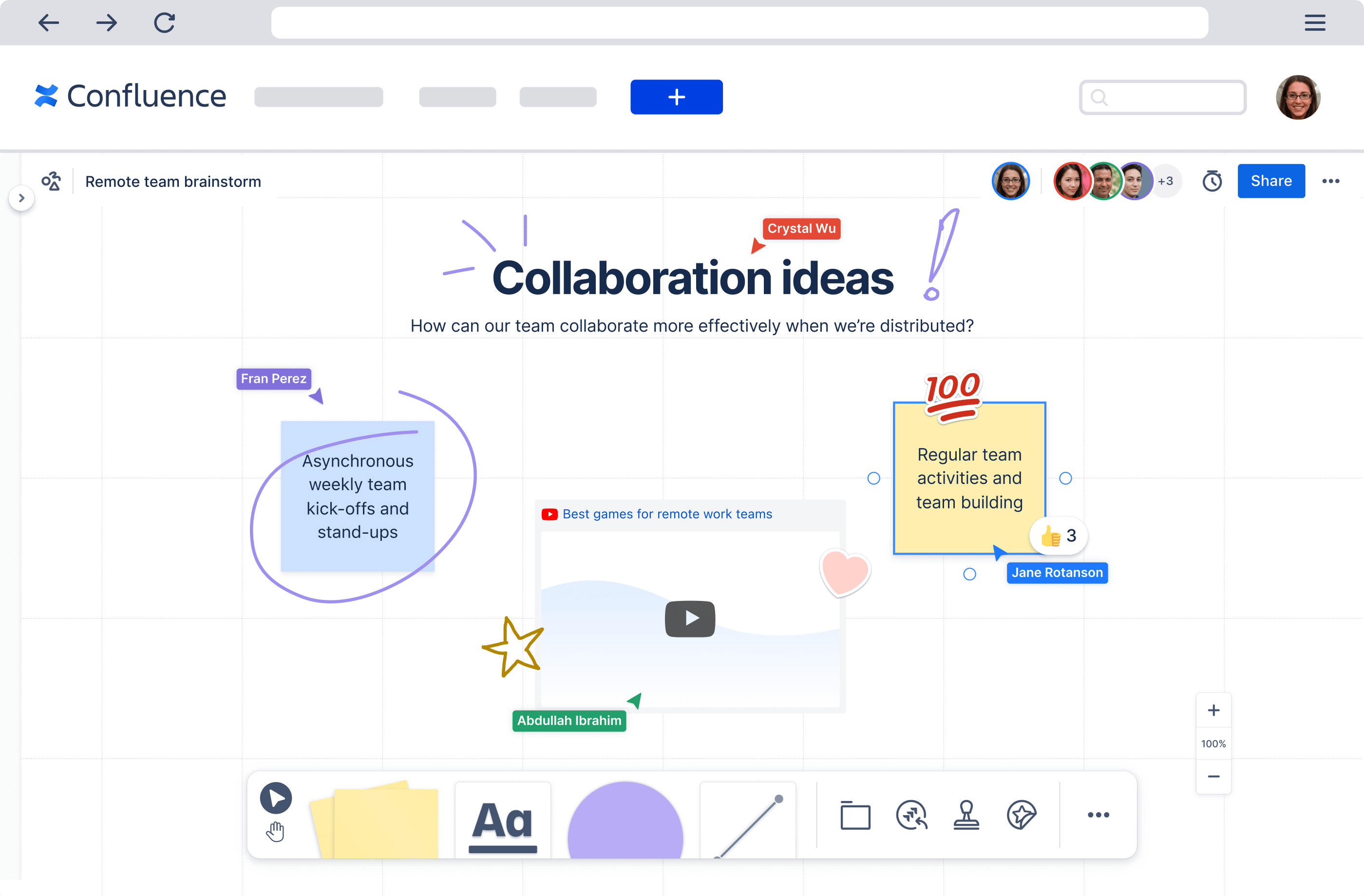
Step 3. Create prototypes to test ideas
Step 3. Create prototypes to test ideas
Prototyping brings abstract concepts into tangible form, allowing teams to test assumptions before investing in full development. Low-fidelity prototypes like paper sketches help explore interaction patterns quickly.
However, high-fidelity prototypes like interactive mockups are useful for testing specific design details and user reactions.
Step 4. Run testing and refine based on results
Step 4. Run testing and refine based on results
Testing prototypes with real users reveals gaps between designers' intentions and users' realities. Methods such as usability testing, A/B experiments, and beta releases provide data on what's working and what needs improvement.
Multiple rounds of testing and refinement help teams iterate toward solutions that truly serve user needs.
Step 5. Finalize design specifications & prepare for production
Step 5. Finalize design specifications & prepare for production
The final phase turns validated prototypes into production-ready products through detailed specification, quality assurance, and launch planning. This involves working closely with engineering teams to prepare marketing materials, user onboarding experiences, and support documentation.
These materials will be critical for you throughout the product development process. That’s why product designers often use specialized product development software to coordinate these activities.
What’s better?

Product management tools that harness the power of AI, like Rovo, make this process even more seamless. Product designers can use AI summary and writing features to quickly give context between tasks and products, so documentation links to its original source.
Common challenges in product design and how to overcome them
Product design projects rarely go exactly as planned, and that's normal. Here are the most common obstacles teams encounter and practical ways to handle them:
Cost limitations and budget constraints: These constraints often force teams to cut corners or abandon promising features. Combat this by creating detailed cost estimates early in the process and establishing clear priorities with stakeholders. Use rapid prototyping to test expensive features cheaply before committing resources, and consider phased rollouts that spread costs over time.
Stakeholder alignment issues: These problems emerge when different departments have conflicting priorities or visions for the product. Regular check-ins with cross-functional teams, shared documentation of decisions and rationale, and clear communication channels help keep everyone aligned. Design thinking workshops can bring stakeholders together to collaborate on solutions rather than debate preferences.
Rapidly changing market trends and user expectations: These challenges can make yesterday's innovative design feel outdated before launching. Stay ahead by building flexibility into your design system, conducting ongoing user research throughout development, and maintaining close connections with customer support teams who hear feedback first. Agile design methodologies allow teams to pivot quickly when trends shift.
Streamline the product design process with Jira Product Discovery
Managing the entire product design process requires coordinating research insights, design iterations, stakeholder feedback, and development handoffs across multiple team members and timelines.

Jira Product Discovery is a centralized platform where teams capture ideas, prioritize features, and track progress from initial concept through launch. Integrate seamlessly with existing agile product management workflows while providing visibility into how business objectives and user needs influence design decisions.
Get started by helping teams avoid common pitfalls, such as losing track of research insights, duplicating work, or misaligning with product development strategy. Connect design activities to product roadmaps and success metrics, teams can make better decisions about where to spend their time.
The result is a faster, more effective product design that consistently delivers value to both users and the business.
Recommended for you
Templates
Ready-made Jira templates
Browse our library of custom Jira templates for various teams, departments, and workflows.
Product guide
A comprehensive introduction to Jira
Use this step-by-step guide to discover essential features and the best practices to maximize your productivity.
Git Guide
Understanding the Basics of Git
From beginners to advanced experts, use this guide to Git to learn the basics with helpful tutorials and tips.