What is IT support?
ITIL Service Strategy & ITIL Processes
You're a problem solver, right? Well, what if someone told you to stop focusing on IT problems in your business and instead think about a set of services you could deliver that would encompass all your IT problems? Fortunately, this thought experiment does not need to go far. In the late 1980’s a group of IT professionals decided to focus less on incoming problems and instead agree upon a fixed set of services that their IT department could provide to customers. They documented this transition and were so wildly successful that they decided to share their process with the world.
Their processes are known as the Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL), ITIL is the most widely accepted approach to ITSM and can help IT organizations deliver services at better quality and lower cost.
What is the ITIL service strategy?
ITIL Service strategy is the process of identifying what services your IT organization should offer and for what customers. Thanks to the work started back in the 80’s, ITIL service strategy is a complete framework that helps organizations align IT services with business objectives and customer needs. This framework helps organizations design, develop, deliver, and manage those services in an efficient and cost-effective manner. Creating a service strategy is the first phase in the ITIL service lifecycle, and is comprised of 5 processes
5 ITIL service strategy processes
Strategy management
When was the last time you did research? While it may not be a hat you’ve worn recently, research is the first step in the strategy management process. Start by assessing your current offerings as an IT org and your unique capabilities. Quick market research can identify opportunities in the broader competitive landscape. Internally, you can learn what needs and constraints exist in your business so that you can offer services that match your organizational goals. This process of aligning IT services to your market and organization is called strategy management.
There are two outcomes in strategy management for IT services. First is the set of services your IT org commits to deliver. This set of services is a blend of your business needs, the market opportunity, and your IT team’s unique skills. The second outcome of strategy management is an implementation plan. For each of the services you plan to offer, your strategy makes clear the teammates, resources, and processes to get work done.
Service portfolio management
After strategy management, you’ll have a set of services you can offer which is called your “service portfolio.” Service portfolio management is how your team monitors each of the services and ensures continued alignment with business goals. Service portfolio management is an ongoing process that checks actual service usage against the service strategy. In pursuit of continuous improvement, portfolio management ensures that you have the right mix of services to meet required business outcomes at your current level of investment.
Let’s say an IT org commits to deliver laptop setup, mobile device provisioning, network infrastructure management, and cloud security services. After portfolio management, they’d likely have a service desk set up with four options that customers could choose from. For each of their four services, they’d document a workflow, set SLAs, and start tracking performance of each service request. If one offering overwhelmed the team and another was never used, portfolio management would encourage the adjustment of offerings and resources to better meet business needs.
IT financial management
Once you know what you are offering and how you will measure success, you can progress to IT financial management. In this stage you are determining the value of each of your services and building the financial backing needed to sustainably deliver your services. This process includes budgeting, accounting, and collection so that the organization covers costs and generates profit.
This stage benefits from collaboration with finance and accounting teams. A trained accountant can help you run cost-benefit analysis for each service and arrive at your total spending by service. Once you have an accurate picture of your spending, you can identify opportunities for cost-cutting. Budgeting allocates funds to keep your services running and support your overall service strategy. Collection, or charging, is a process for billing customers for what services they use.
Demand management
Anticipating the demand for your services helps you manage your team and your resources. Demand management is a precursor to capacity management. By analyzing, anticipating, and influencing demand for your services, you can ensure you have the right capacity to deliver services effectively.
Analyzing service usage is best aided by service desk ticket data. Additional data points like network and device usage can be used. Your goal in the analysis stage is to understand current use of services. Progressing to the anticipation stage, you shift your focus to forecasting needs, identifying trends, and making predictions about future usage. One of simplest ways to anticipate needs is to talk with business leaders from around the business. Influencing demand for your services is another powerful tool to limit risks and expenses. Many IT teams influence demand by clearly communicating which services they will and will not offer.
Business relationship management
One of the most refreshing parts of ITIL service strategy is business relationship management. This is where you step back from a focus on your services and refocus on maintaining positive relationships with internal teams, employees, and any other customers you might have. The simplest way to stay focused on relationship management is customer satisfaction data. Many teams are using automated polling features in their service desk software to keep this data top of mind. Setting goals around relationship management can help align the team around positive outcomes.
Another strategy for business relationship management is revisiting the needs and business objectives that originally inspired your service strategy. By talking individually with team and business leaders, you can go one click deeper into their needs and identify adjustments you could make to better serve those needs. While the outcome of these conversations is useful in itself, many IT leaders find that having those conversations strengthens relationships more than simply solving problems.
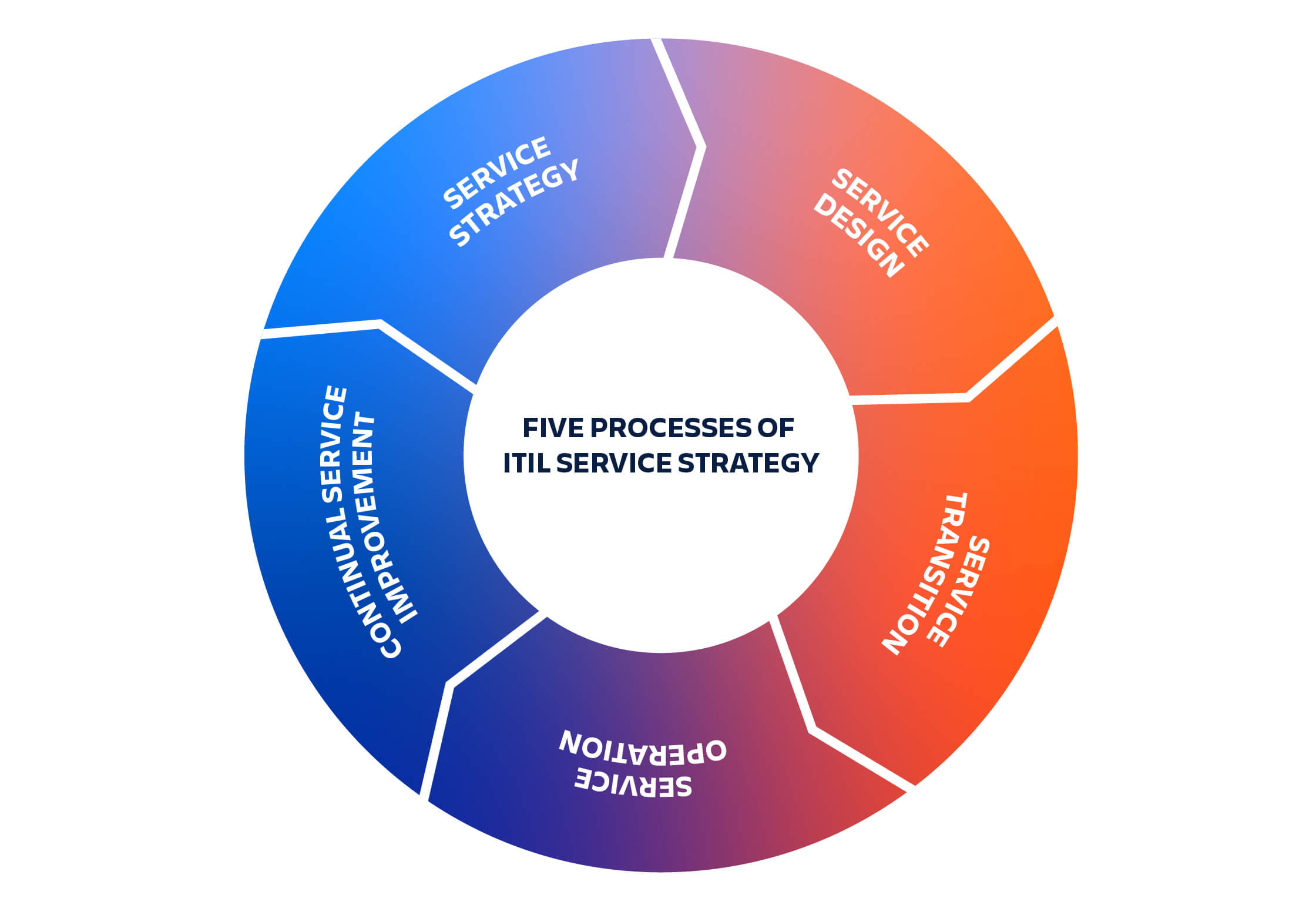
ITIL service lifecycle
A useful way to learn more about your service strategy is to understand how service strategy fits into the ITIL service lifecycle. ITIL provides guidelines and best practices for implementing a five phase IT service lifecycle: Service strategy, design, transition, operations, and continual improvement. Investment in a strong service strategy provides a solid foundation for the remaining four phases. Image showing the five phases of the ITIL lifecycle. Most competitors show these on a wheel with attempts to convey that Continual service improvement is an ongoing process. Examples:
Service strategy
If you’ve read this far you know all about service strategy. Nice! Service strategy is the identification of what services your IT organization should offer and for what customers. In this foundational phase, you strategize the development, delivery, and management of those services in an efficient and cost-effective manner. Service strategy is executed in five processes: Strategy management, service portfolio management, IT financial management, demand management, and business relationship management.
Service design
Service design is the process of designing new services and improving existing ones. Service design is an exceptionally well documented process that will encourage you to consider the four fundamental components of a healthy service: People, products, partners, and processes. By using the four P’s and eleven service design processes, you can effectively design the services in your service strategy.
Service transition
Service transition is the process of building and deploying services. Service transition is where your service strategy and service design come to life. It’s exciting to spin up the tools and systems needed to execute each of your services. Strong service transition teams use eight ITIL processes to build today’s vision for your services and lay the groundwork for potential changes in the future. Service transition is a process to revisit as you learn, grow, and adapt to changing business needs.
Service operation
The objective of ITIL Service Operation is to make sure that IT services are delivered effectively and efficiently. Teams that have successfully implemented an ITIL service lifecycle spend most of their time here in operations. This is where problem solvers get to solve problems! Service operation handles tickets, user requests, resolving service failures, and routine operational work. Being heads down in service operation is a joy you can look forward to thanks to the ITIL service lifecycle.
Continual service improvement
The goal of continual service improvement is exactly what you might think. This is where you learn from past successes and failures. Four ITIL processes will help you continually improve the effectiveness and efficiency of your services. Starting with a service review, you then evaluate your current processes, define improvement initiatives, and commit to monitoring those initiatives. With this process, your team can introduce improvements where necessary.
Managing ITIL service strategy processes with Jira Service Management
Service strategy concepts in this article are the foundation for your service lifecycle. To move though this lifecycle, you’ll need tools that support the implementation of these concepts. Let’s discuss some of the features of Jira Service Management and how they aid in implementation. An added bonus? Jira Service Management is ITIL Certified.
Incident and problem management
When things go awry, a tool can bring your IT operations teams together to rapidly respond to, resolve, and continuously learn from incidents. In Jira Service Management, you can group incidents into problems, fast-track root cause analysis, and record workarounds to minimize the impact of incidents. ITIL is focused on services and one of the most common services offered is incident management. Tools to aid in the resolution of problems will help your service strategy shine.
Change management
Change is hard. Jira Service Management works to empower your IT operations teams with richer contextual information around changes so they can make better decisions. More than just a change request, a good tool will set up approval workflows, risk assessment, and deployment tracking. We learned that service deployment is about building and changing your services and this is how you manage those changes.
Configuration management
Part of your service strategy is the implementation plan. A tool like Jira Service Management will help you gain visibility into the infrastructure that supports critical applications and services. Understanding these service dependencies will help you minimize risk. By being able to anticipate the downstream impact of changes, your teams can rapidly resolve incidents when they do occur.
Request management
A service management tool can manage work across teams with one platform so your employees and customers quickly get the help they need. You can tailor request forms to meet each team's unique requirements and bring together requests from email, chat tools, your service desk, and other channels. SLAs, a knowledge base, and customer feedback tools will help you stay on top of business relationship management and focus on what your team does best.
Atlassian's guide to agile ways of working with ITIL 4
ITIL 4 is here—and it’s more agile than ever. Learn tips to bring agility and collaboration into ITSM with Atlassian.
Read the whitepaperWhat is a service request?
Service Request Management enables IT teams to quickly and easily fulfill customer requests. Check out the process and best practices.
Read the article