Git subtree: the alternative to Git submodule

NICOLA PAOLUCCI
Developer Advocate
The Internet is full of articles on why you shouldn’t use Git submodules. While submodules are useful for a few use cases, they do have several drawbacks.
Are there alternatives? The answer is: yes! There are (at least) two tools that can help track the history of software dependencies in your project while allowing you to keep using Git:
git subtree- Google repo
In this post we will look at git subtree and show why it is an improvement – albeit not perfect – over Git submodule.
What is Git subtree, and why should I use it?
git subtree lets you nest one repository inside another as a sub-directory. It is one of several ways Git projects can manage project dependencies.
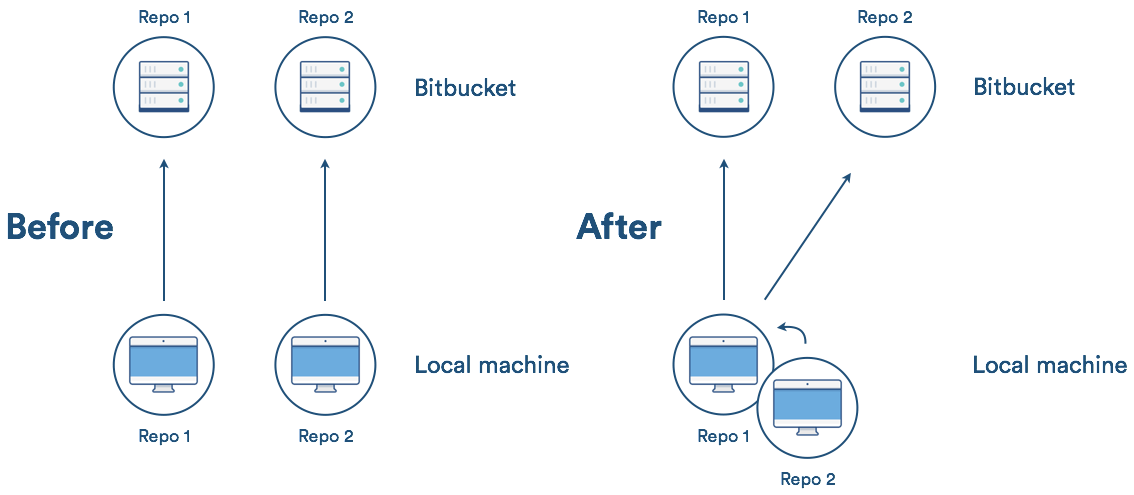
Why you may want to consider git subtree
- Management of a simple workflow is easy.
- Older version of Git are supported (even older than v1.5.2).
- The sub-project’s code is available right after the clone of the super project is done.
git subtreedoes not require users of your repository to learn anything new. They can ignore the fact that you are usinggit subtreeto manage dependencies.git subtreedoes not add new metadata files like Git submodule does (i.e., .gitmodule).- Contents of the module can be modified without having a separate repository copy of the dependency somewhere else.
Drawbacks (but in our opinion they're largely acceptable):
- You must learn about a new merge strategy (i.e.
git subtree). - Contributing code back upstream for the sub-projects is slightly more complicated.
- The responsibility of not mixing super and sub-project code in commits lies with you.
related material
How to move a full Git repository
SEE SOLUTION
Learn Git with Bitbucket Cloud
How to use Git subtree
git subtree is available in stock version of Git since May 2012 – v1.7.11 and above. The version installed by homebrew on OSX already has subtree properly wired, but on some platforms you might need to follow the installation instructions.
Here is a canonical example of tracking a vim plug-in using git subtree.
The quick and dirty way without remote tracking
If you just want a couple of one-liners to cut and paste, read this paragraph. First add git subtree at a specified prefix folder:
git subtree add --prefix .vim/bundle/tpope-vim-surround https://bitbucket.org/vim-plugins-mirror/vim-surround.git main --squash(The common practice is to not store the entire history of the subproject in your main repository, but If you want to preserve it just omit the –squash flag.)
The above command produces this output:
git fetch https://bitbucket.org/vim-plugins-mirror/vim-surround.git main
warning: no common commits
remote: Counting objects: 338, done.
remote: Compressing objects: 100% (145/145), done.
remote: Total 338 (delta 101), reused 323 (delta 89)
Receiving objects: 100% (338/338), 71.46 KiB, done.
Resolving deltas: 100% (101/101), done.
From https://bitbucket.org/vim-plugins-mirror/vim-surround.git
* branch main -} FETCH_HEAD
Added dir '.vim/bundle/tpope-vim-surround'As you can see this records a merge commit by squashing the whole history of the vim-surround repository into a single one:
1bda0bd [3 minutes ago] (HEAD, stree) Merge commit 'ca1f4da9f0b93346bba9a430c889a95f75dc0a83' as '.vim/bundle/tpope-vim-surround' [Nicola Paolucci]
ca1f4da [3 minutes ago] Squashed '.vim/bundle/tpope-vim-surround/' content from commit 02199ea [Nicola Paolucci]If after a while you want to update the code of the plugin from the upstream repository you can just do a git subtree pull:
git subtree pull --prefix .vim/bundle/tpope-vim-surround https://bitbucket.org/vim-plugins-mirror/vim-surround.git main --squashThis is very quick and painless, but the commands are slightly lengthy and hard to remember. We can make the commands shorter by adding the sub-project as a remote.
Adding the sub-project as a remote
Adding the subtree as a remote allows us to refer to it in shorter form:
git remote add -f tpope-vim-surround https://bitbucket.org/vim-plugins-mirror/vim-surround.gitNow we can add the subtree (as before), but now we can refer to the remote in short form:
git subtree add --prefix .vim/bundle/tpope-vim-surround tpope-vim-surround main --squashThe command to update the sub-project at a later date becomes:
git fetch tpope-vim-surround main
git subtree pull --prefix .vim/bundle/tpope-vim-surround tpope-vim-surround main --squashContributing back upstream
We can freely commit our fixes to the sub-project in our local working directory now. When it’s time to contribute back to the upstream project, we need to fork the project and add it as another remote:
git remote add durdn-vim-surround ssh://git@bitbucket.org/durdn/vim-surround.gitNow we can use the subtree push command like the following:
git subtree push --prefix=.vim/bundle/tpope-vim-surround/ durdn-vim-surround main
git push using: durdn-vim-surround main
Counting objects: 5, done.
Delta compression using up to 4 threads.
Compressing objects: 100% (3/3), done.
Writing objects: 100% (3/3), 308 bytes, done.
Total 3 (delta 2), reused 0 (delta 0)
To ssh://git@bitbucket.org/durdn/vim-surround.git
02199ea..dcacd4b dcacd4b21fe51c9b5824370b3b224c440b3470cb -} mainAfter this we’re ready and we can open a pull-request to the maintainer of the package.
Can I do this without using the Git subtree command?
Yes! Yes you can. git subtree is different from the subtree merge strategy. You can still use the merge strategy even if for some reason git subtree is not available. Here is how you would go about it.
Add the dependency as a simple git remote:
git remote add -f tpope-vim-surround https://bitbucket.org/vim-plugins-mirror/vim-surround.gitBefore reading the contents of the dependency into the repository, it’s important to record a merge so that we can track the entire tree history of the plug-in up to this point:
git merge -s ours --no-commit tpope-vim-surround/mainWhich outputs:
Automatic merge went well; stopped before committing as requestedWe then read the content of the latest tree-object into the plugin repository into our working directory ready to be committed:
git read-tree --prefix=.vim/bundle/tpope-vim-surround/ -u tpope-vim-surround/mainNow we can commit (and it will be a merge commit that will preserve the history of the tree we read):
git ci -m"[subtree] adding tpope-vim-surround"
[stree 779b094] [subtree] adding tpope-vim-surroundWhen we want to update the project we can now pull using the git subtree merge strategy:
git pull -s subtree tpope-vim-surround mainGit subtree is a great alternative
After having used Git submodules for a while, you'll see git subtree solves lots of the problems with Git submodule. As usual, with all things Git, there is a learning curve to make the most of the feature.
Take a look at this article on the power of Git subtree.
Share this article
Next Topic
Recommended reading
Bookmark these resources to learn about types of DevOps teams, or for ongoing updates about DevOps at Atlassian.
Bitbucket blog
DevOps learning path
