How knowledge management works in Jira Service Management
Overview
Knowledge management is the process of creating, curating, sharing, using, and managing knowledge across an organization.
A knowledge base is the foundation of a knowledge management practice. It’s a self-serve online library of information about a product, service, department, or topic, including FAQs and troubleshooting guides.
Jira Service Management’s out-of-the-box knowledge base enables your service teams to easily manage and share knowledge so that the right answers are always at your fingertips. This powerful and flexible tool leverages the power of Confluence, enabling your team to create and curate articles directly within your Jira Service Management project.
Here are some ways you can use a knowledge base in Jira Service Management to benefit your teams and customers:
- Document answers to frequently asked questions to save agents’ time.
- Empower customers to help themselves by searching for resolutions in the help center.
- Gather customer feedback to lead to more relevant and helpful article updates.
- Help agents solve requests faster by sharing articles with customers or referencing articles while they work.
- Encourage agents to create new articles if a request requires a new resolution.
- Standardize answers to customer questions instead of offering multiple responses from different sources.
The knowledge management process:
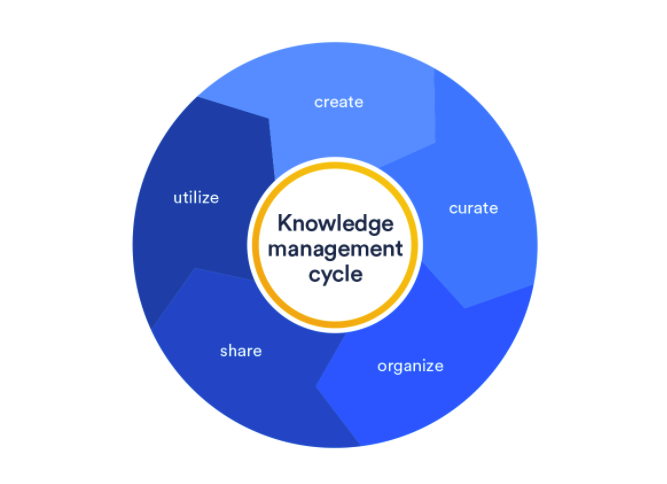
Knowledge management is an ongoing responsibility. Even after you’ve implemented a system, there’s a constant cycle of adding new material and eliminating items that are outdated, as well as the discovery of hidden knowledge.
A key component of knowledge management is the implementation of a knowledge base. Here are our recommendations to manage this process:
1. Determine if you need one
Start by asking yourself how much time you’d save if employees didn’t have to answer the same questions over and over. Then look at your customer satisfaction and productivity goals; if your organization could do better, a knowledge base is a great place to start.
2. Get your content together.
This is no easy task -- content is everywhere. Collect FAQs (and answers) from any department that provides service. And we mean any department, like the teams who build trade shows, the people in IT, HR. All teams can and should contribute to your knowledge base. And they should be part of the knowledge management process that maintains it.
3. Customize pages. Stay consistent.
Create a style guide, so that all of the information you pour into your knowledge base looks and sounds the same. This covers the entire visual presentation including font, type size, colors, and even images.
4. Find your voice. And stick with it.
Figure out how your company or organization talks. Whether you’re polished or have a laid back vibe, use that in the presentation of your knowledge base. The people in marketing can help.
5. Make it easy. And keep it that way.
Once it’s up and running, remember that your knowledge base is a self-serve operation. You’ll need to make sure your knowledge base is easy to navigate. And easy to use. Use labels and search terms to categorize information and make articles easier to find. Organize the content to fit your organization and then be careful to maintain it.
6. Keep it relevant. And up to date.
This is where the creation of your knowledge base flows into the ongoing task of knowledge management. Implement a system of analytics, so you understand how people are using your content. Allow users to leave feedback and ratings. Make sure your management and marketing people have a say in managing the knowledge base. Avoid delays and bottlenecks by identifying multiple people to approve content. Set up gatekeepers, then empower them to act when information needs to be dropped, added or changed.
For more information, check out our Knowledge Management page.
How to get started with knowledge management in Jira Service Management
How to set up your knowledge base in Jira Service Management
If you don’t already have Confluence on your site:
To set up your knowledge base in Jira Service Management, at a minimum, you’ll need to have a Free plan of Confluence on the same site.
To add Confluence to your site from your service project, select Knowledge base from your project sidebar navigation and follow the prompts. This will ensure that the Confluence features you need for knowledge management will be available directly in Jira Service Management.
If you already have Confluence on your site:
To have all your drafts and published pages from your existing Confluence spaces appear in your service project, you’ll need to link your knowledge base spaces to your service project.
How to create a knowledge base article
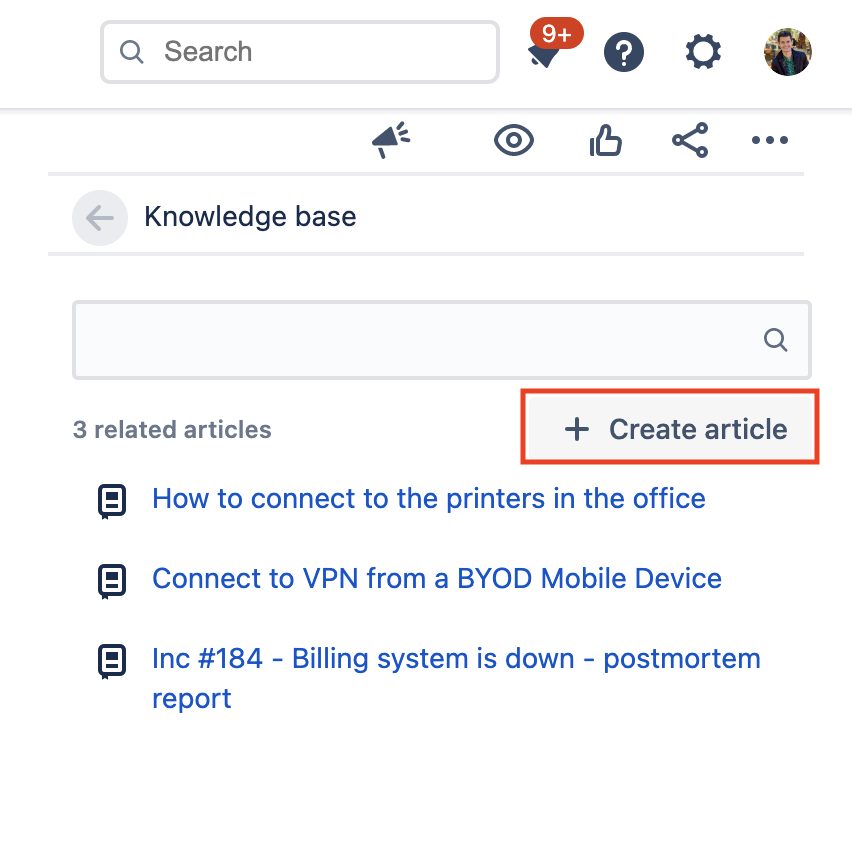
Next, it’s time to add articles to your knowledge base to help customers help themselves. Articles can be created from your knowledge base project settings, or directly from a request when interacting with a customer.
To create a knowledge base article from knowledge base project settings:
- From your service project, select Knowledge base in the sidebar menu.
- Select Create article.
- Select a linked knowledge base space for your article to live.
- Create and publish your article.
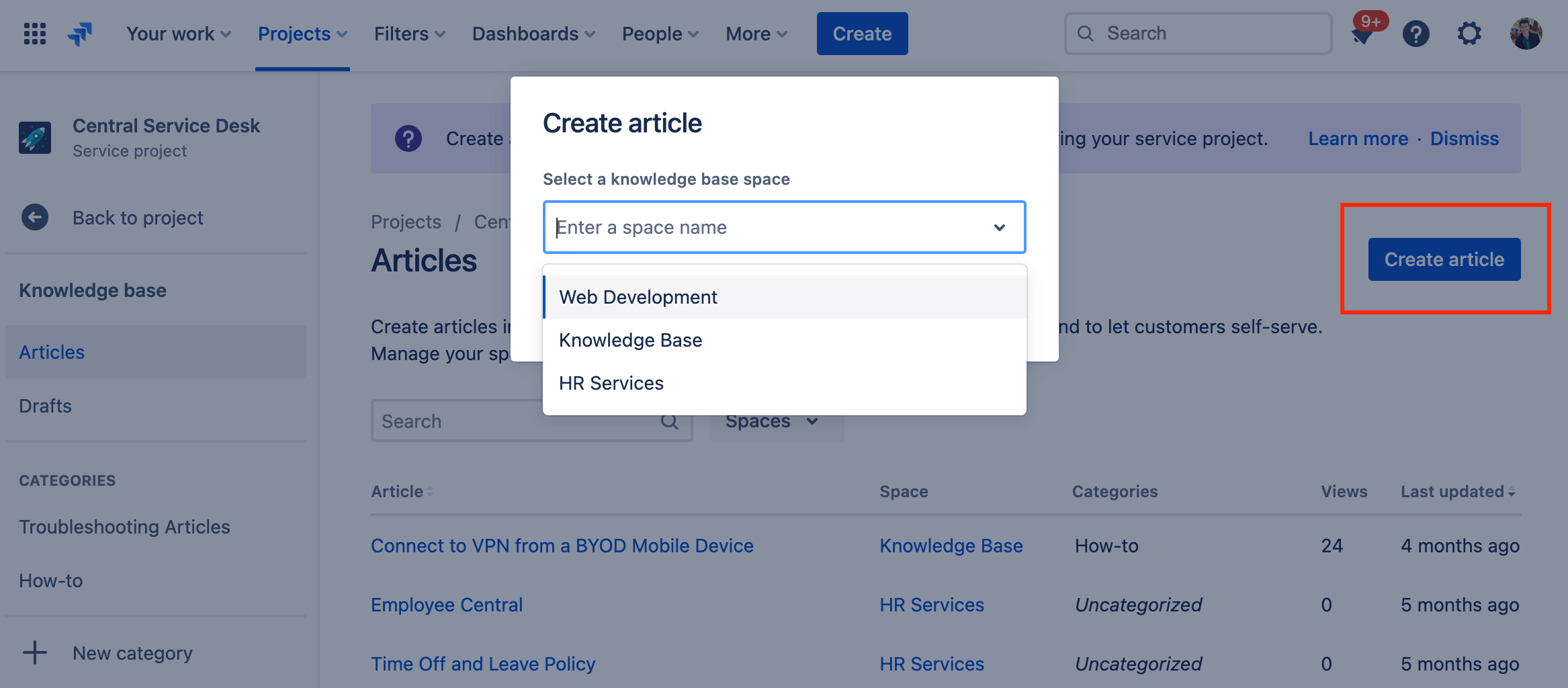
Note that if you start the article creation process and don’t publish the article, it will be saved in your drafts.
To create a knowledge base article from a request:
Additionally, if an agent is looking for an article when viewing a request and comes up short, they can easily create new articles from the useful information in a request. To create a knowledge base article from a request:
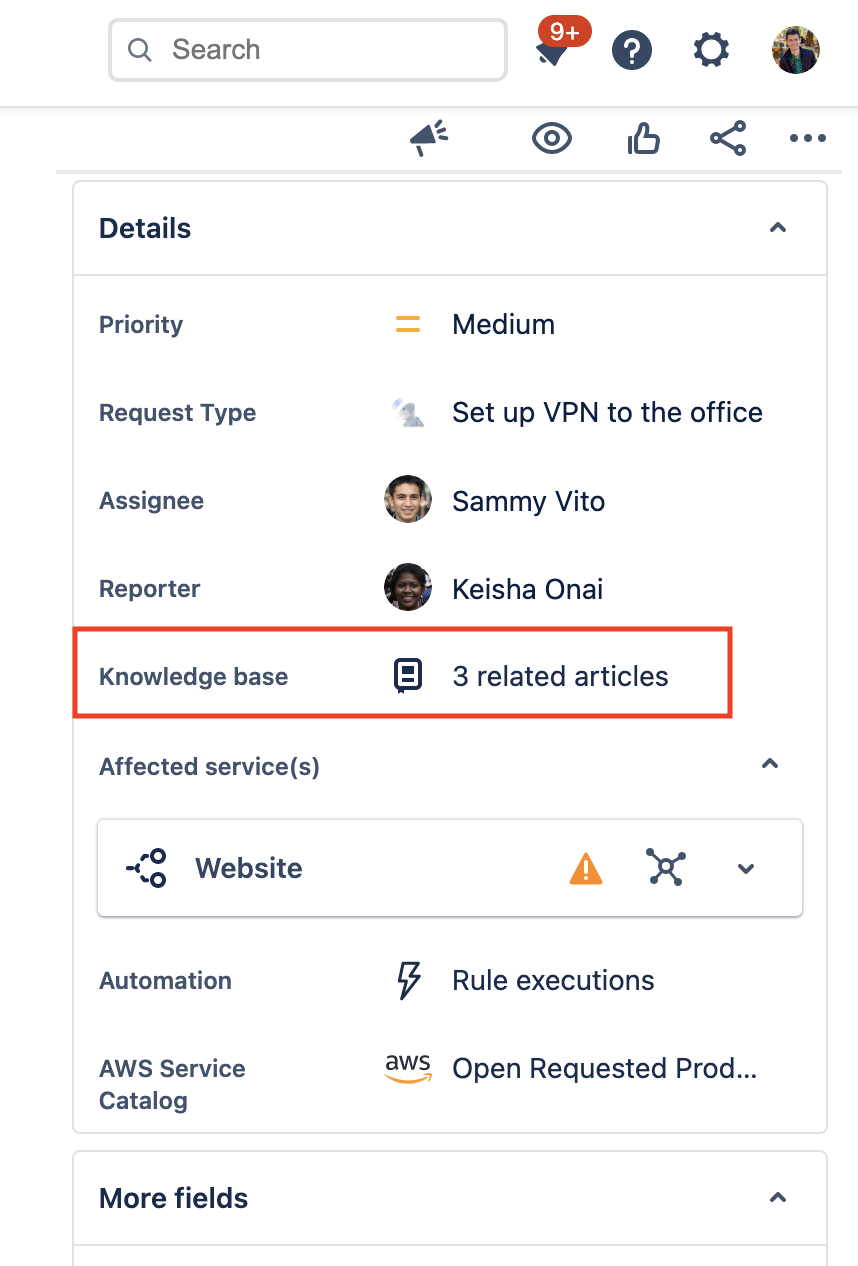
- Locate the Details section of the request.
- Select related article(s) under Knowledge base.
- Select Create article and fill out the required information.
How to review your knowledge base reports
Once your knowledge base has been configured, use Jira Service Management’s native knowledge base reporting to find out which articles are receiving the most views and positive feedback. There are two key knowledge base reports:
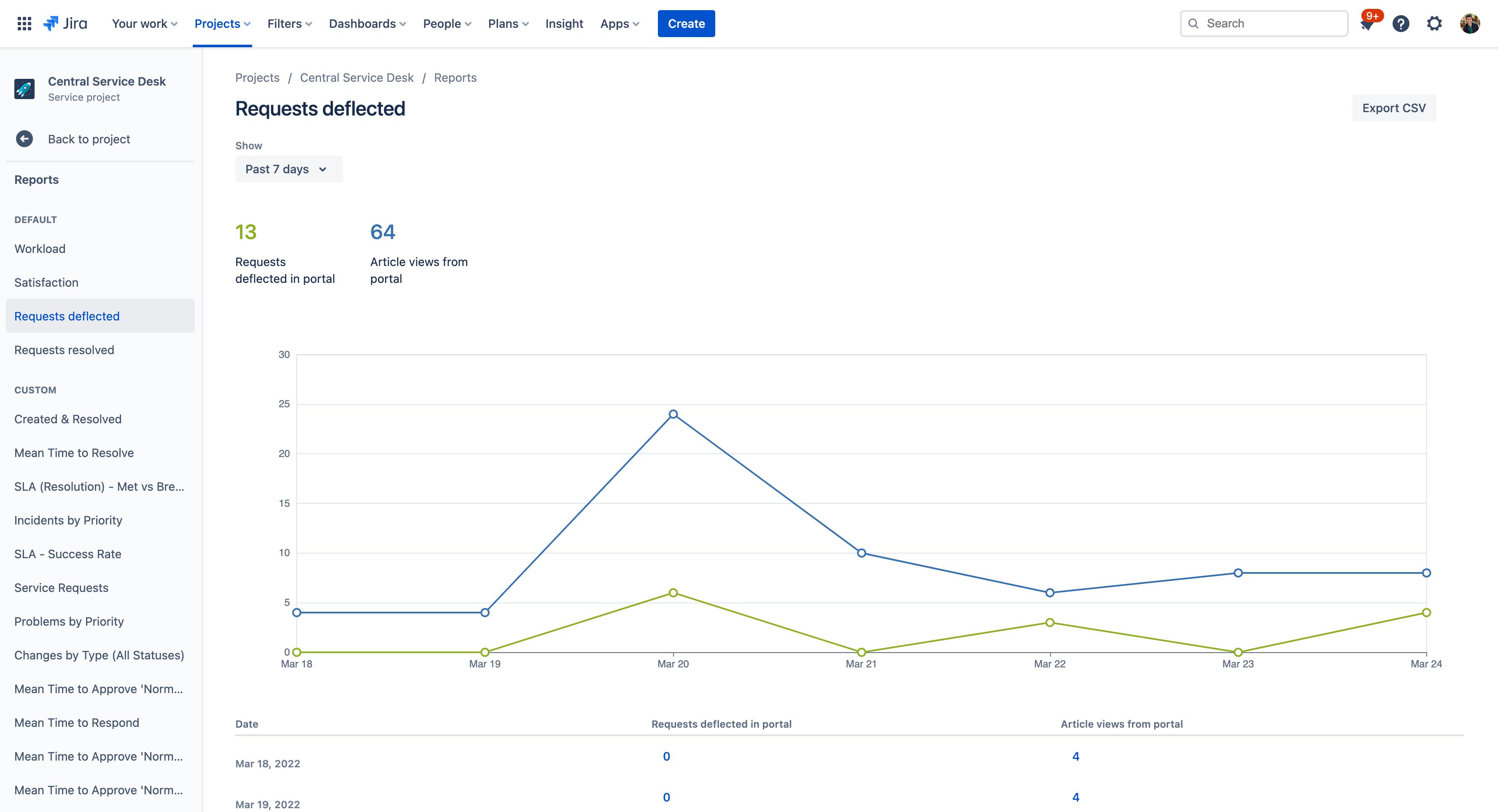
1. Requests deflected
This report shows how often customers found your knowledge base articles helpful. This includes the number of requests deflected in the portal and the number of article views in the portal. When a customer goes to a request form and starts writing the summary, knowledge base articles are surfaced based on the customer’s search. If the customer selects an article from a request form and votes it as helpful, it is considered as a request that was deflected in the portal.
2. Requests resolved
This report shows a breakdown of how your requests are being resolved. The report includes the number of requests resolved with an article, without an article, and which requests were deflected in the portal. If a resolved request has one or more links to knowledge base articles in its comments, it is considered as a request resolved with an article. If no article links are used to answer a request, it is considered a request resolved without an article.
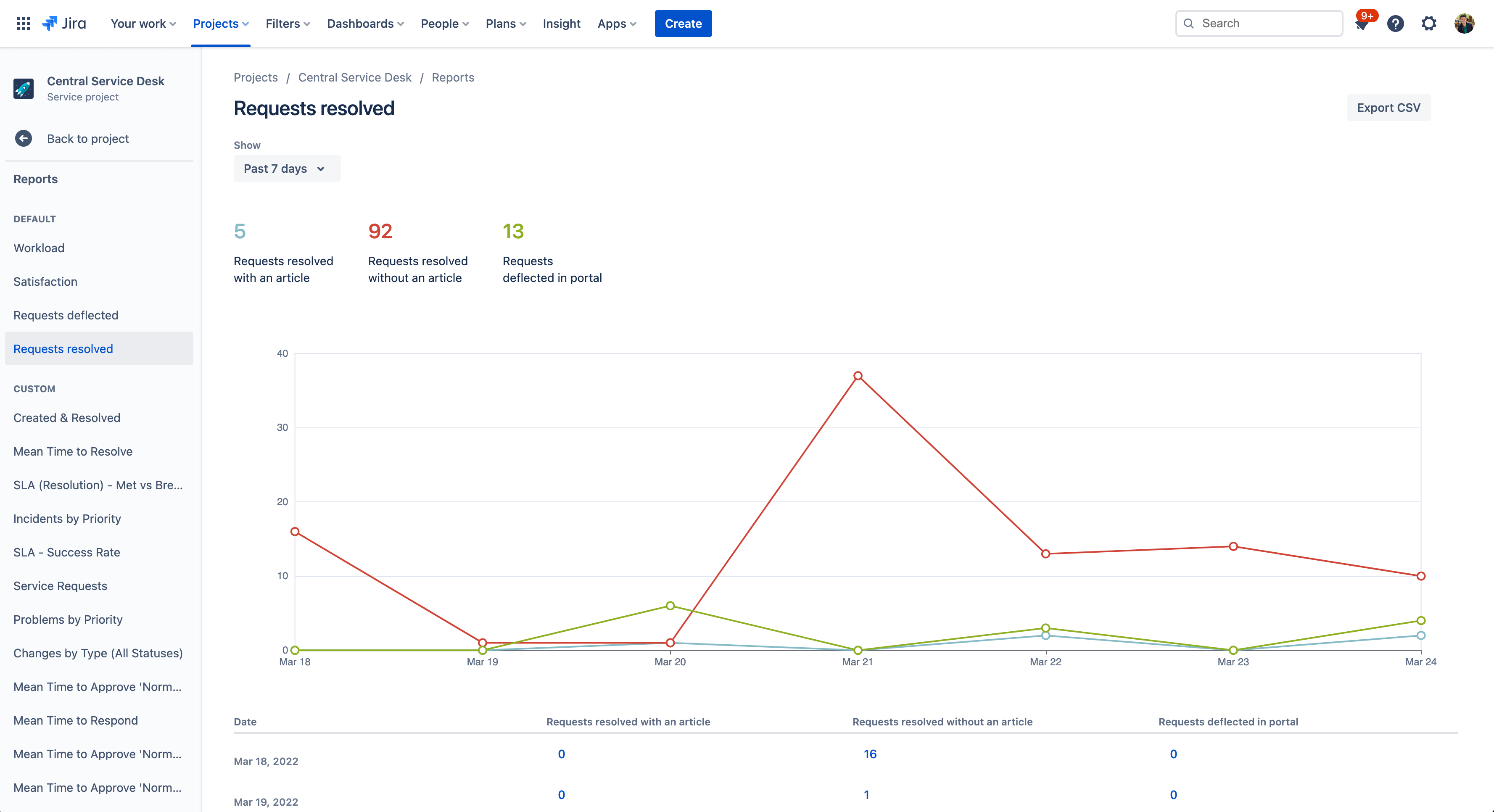
To access knowledge base reports:
- Navigate to your Jira Service Management project.
- Select Reports in the left-hand menu.
- Select Requests deflected or Requests resolved to view the reports.
- Use the “show” filter to change your report date range.
Knowledge management best practices and tips
Expand your knowledge base capabilities with a paid Confluence plan
In addition to Jira Service Management’s out-of-the-box knowledge base powered by Confluence, customers can subscribe to a paid Confluence plan for even more knowledge base capabilities, including:
- Over 70 templates that allow you to predefine and standardize content for your internal and external users.
- In-line comments and @ user mentions
- Article comments and attachments
- Space and page permissions.
Create a culture focused on knowledge sharing
Knowledge should be easy for your entire organization to search, find, and create. Encourage team members to actively create and edit pages. Recognize the authors with rewards to encourage team members to contribute to the knowledge base and improve customer satisfaction.
Focus on brief articles or answers
Shared documentation does not always mean shared understanding. Rather than creating long, expansive documents, tailor your content to your team. Your entire team and customers can learn and absorb information faster when it's quick to consume, uses easy-to-understand language, and is published in a timely matter.
Getting Started
Enterprise Service Management
Getting Started
Asset and Configuration Management